FDA Issues Complete Response Letter for Cosibelimab in Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The FDA did not raise any concerns about the clinical data package, safety, or labeling for the approvability of cosibelimab for squamous cell carcinoma.
The application was based on the global, multicenter, multicohort, pivotal phase 1 CK-301-101 trial (NCT0321240), which assessed the efficacy of cosibelimab in patients with select advanced cancers.
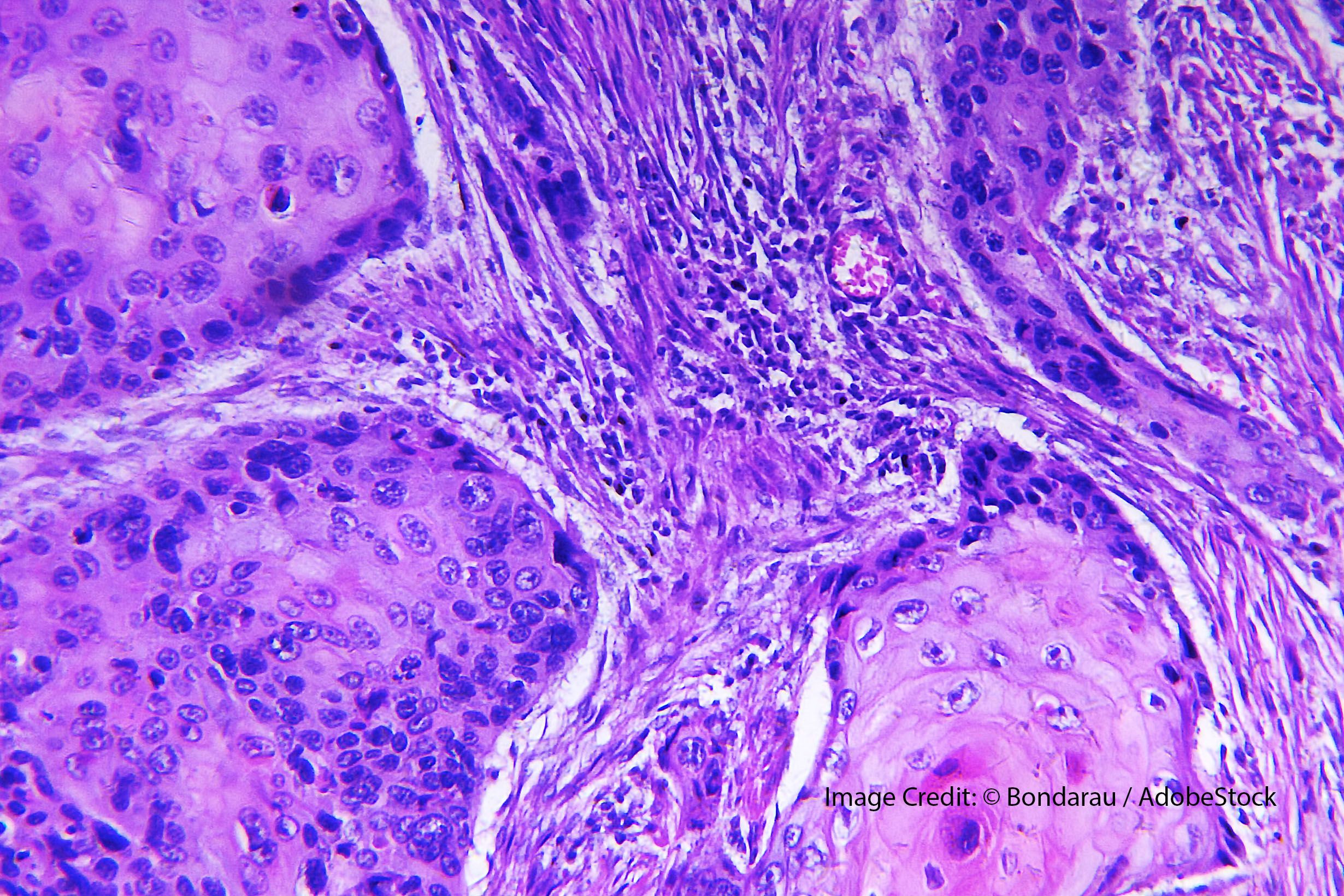
The FDA has issued a complete response letter (CRL) to a biologic license application (BLA) for cosibelimab (CK-301) as a treatment option for patients with metastatic or locally advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC) who are not candidates for curative surgery or radiation, according to a press release from Checkpoint Therapeutics Inc.1
The letter referenced findings that were based on a multi-sponsor inspection of Checkpoint’s third-party contract manufacturing organization, which cited approvability issues that needed to be addressed in a resubmission. There were no concerns regarding the clinical data package, safety, or labeling of the drug.
Checkpoint Therapeutics Inc. intends to resubmit a BLA for cosibelimab by next year.2
“As the only deficiencies relate to the FDA’s inspection of our third-party contract manufacturing organization, we believe we can address the feedback in a resubmission to enable marketing approval in 2024,” James Oliviero, president and chief executive officer of Checkpoint Therapeutics, said in the press release.1 “We are committed to working closely with our third-party manufacturer and the FDA on our resubmission to make cosibelimab available to patients living with CSCC.”
The BLA filing was originally accepted by the FDA in March 2023, and the Prescription Drug User Fee Act date was set for January 3, 2024.3 The application was based on the global, multicenter, multicohort, pivotal phase 1 CK-301-101 trial (NCT0321240), which assessed the efficacy of cosibelimab in patients with select advanced cancers.
Patients over the age of 18 with a life expectancy of over 3 months and an ECOG status of 0 or 1 who had metastatic CSCC not amenable to local therapy were eligible to participate in the trial.4 Patients received 800 mg of intravenous cosibelimab every 2 weeks until complete response (CR), progressive disease, unacceptable toxicity, or clinical deterioration. Patients then entered follow up post treatment.
The study’s primary end point was confirmed objective response rate (ORR) assessed by independent central review according to RECIST version 1.1 criteria, and the key secondary end point was duration of response.
Results showed that among 78 patients who were treated with cosibelimab, the confirmed ORR was 47.4% (95% CI; 36.0%- 59.1%); this included 6 CRs and 31 partial responses. The median duration of response (DOR) was not reached at the time of data cutoff, with an estimated 24-month DOR rate of 73.0% (95% CI, 54.2%-85.0%).
Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) of any grade were reported in 97.4% of patients, with high-grade TEAEs occurring in 52.6%. Common TEAEs included fatigue (26.9%), rash (16.7%), and anemia (15.4%).
References
- U.S. food and drug administration issues complete response letter for cosibelimab solely due to inspection findings at third-party manufacturer. News release. Checkpoint Therapeutics, Inc. December 18, 2023. Accessed December 18, 2023. https://tinyurl.com/5yewpx4b
- Checkpoint therapeutics gets FDA response letter on cosibelimab application. News release. MarketWatch. December 18, 2023. Accessed December 18, 2023. https://tinyurl.com/3d5zd54u
- Checkpoint therapeutics announces FDA filing acceptance of biologics license application for cosibelimab in metastatic or locally advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. News release. Checkpoint Therapeutics, Inc. March 02, 2023. Accessed December 19, 2023. https://tinyurl.com/wc7vs9pu
- Clingan PR, Brungs D, Arnold S, et al. Efficacy and safety of cosibelimab, an anti–PD-L1 antibody, in patients with metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40(suppl 16):9537-9537. doi:10.1200/jco.2022.40.16_suppl.9537
How Supportive Care Methods Can Improve Oncology Outcomes
Experts discussed supportive care and why it should be integrated into standard oncology care.