Rituximab Plus CHOP Is Superior to CHOP Alone in Elderly Patients With Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Interim Results of a Randomized GELA Trial
A total of 400 previously untreated elderly patients (aged 60 to 80) with stage II to IV diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLCL) were recruited to an open-label, randomized study of standard CHOP (cyclophosphamide [Cytoxan, Neosar],
A total of 400 previously untreated elderly patients (aged 60 to 80) with stage II to IV diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLCL) were recruited to an open-label, randomized study of standard CHOP (cyclophosphamide [Cytoxan, Neosar], doxorubicin HCl, vincristine [Oncovin], prednisone) every 3 weeks for 8 cycles vs standard CHOP with rituximab (Rituxan) at 375 mg/m2 on day 1 of each cycle (R-CHOP). Patients were stratified for age-adjusted International Prognosic Index (IPI) scores (0-1 vs 2-3), had performance status (PS) 2, and no contraindication to doxorubicin. The primary end point was event-free survival, with events defined as disease progression or relapse, death, or initiation of new alternative treatment.
A planned interim analysis has been conducted, including data from 328 patients, 159 in the CHOP arm and 169 in the R-CHOP arm. The stopping date was June 1, 2000. Median age of patients was 69 years. Adverse prognostic parameters were equally distributed between arms: 63% of patients had stage IV disease, 19% had PS > 1, 65% had elevated lactate dehydrogenase, 26% had bone marrow involvement, 52% had more than one extranodal disease site, and 60% had IPI scores of 2 or 3. An independent panel reviewed 86% of the cases and DLCL histology was confirmed in 87%. Sixty-two patients withdrew early, 23 due to treatment failure (18 with CHOP, 5 with R-CHOP), 30 due to adverse events (17 with CHOP, 13 with R-CHOP), and 9 for other reasons.
Preliminary analysis revealed no major difference between the two arms in hematologic toxicity, or in grade 3 or 4 infection, mucositis, vomiting, liver, cardiac, neurologic, renal, or lung toxicity. Eighteen patients had a grade 3 or 4 infusion-related syndrome during the first rituximab infusion. With a median follow-up of 12 months, 77 events (48%) were observed in the CHOP arm and 49 (29%) in the R-CHOP arm. Interim results based on data from all 328 patients (intent-to-treat analysis) were as follows:
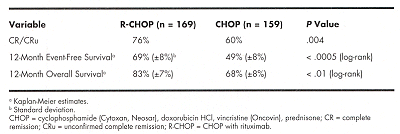
CONCLUSION: This study demonstrated that the addition of rituximab to CHOP chemotherapy led to significant prolongation of event-free survival and overall survival in elderly patients with DLCL, without significant additional toxicity.
Click here to read Dr. Bruce Cheson's commentary on this abstract.
Highlighting Insights From the Marginal Zone Lymphoma Workshop
Clinicians outline the significance of the MZL Workshop, where a gathering of international experts in the field discussed updates in the disease state.