17 A Clinical Systematic Literature Review of Treatments Among Patients With Advanced/ Metastatic HER2+ Breast Cancer
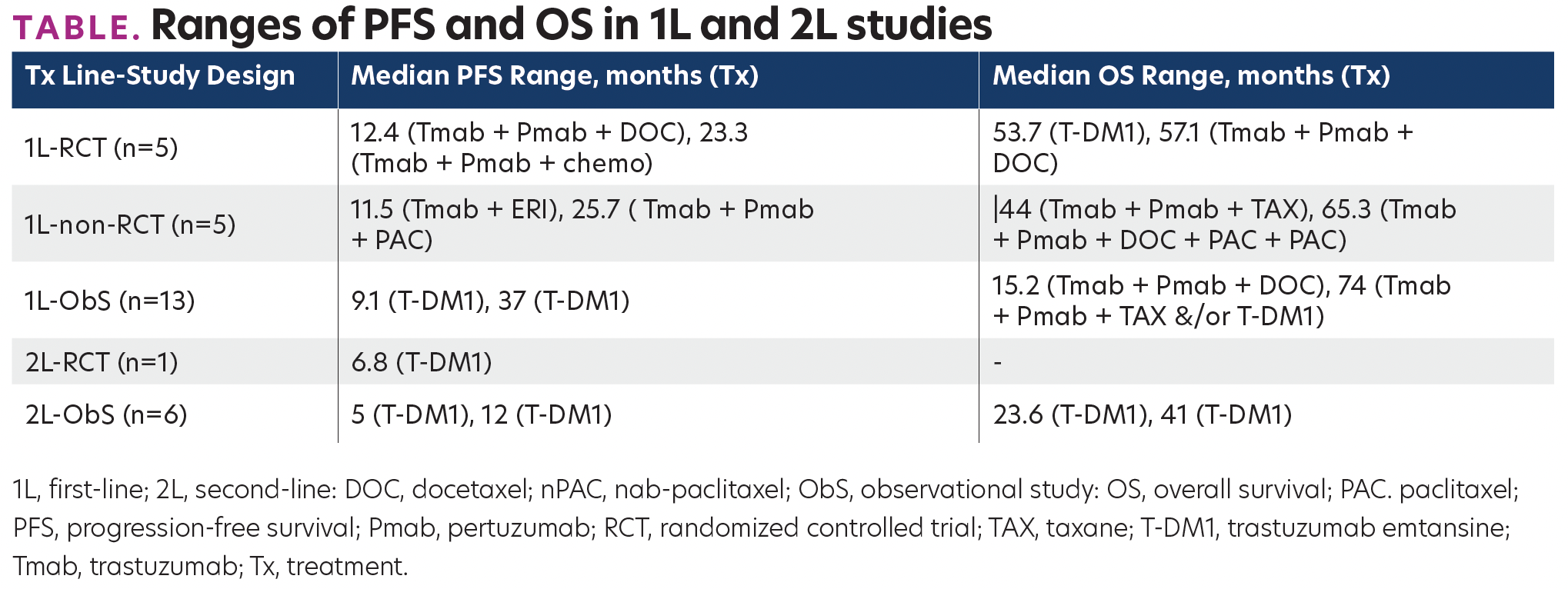
TABLE. Ranges of PFS and OS in 1L and 2L studies
Background
The incidence of breast cancer (BC) has continued to rise rapidly and is a leading cause of cancer death. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–positive (HER2+) BC is approximately 20% of all invasive BC. Recent advances in chemotherapy and targeted treatments against HER2 have significantly improved the prognosis of HER2+ BC. Pertuzumab (Pmab) + trastuzumab (Tmab) + docetaxel (DOC) has been approved for the first-line (1L) treatment of patients with HER2+ metastatic BC. It is currently regarded as the standard of care in this indication. Eribulin mesylate (ERI, Halaven®), a nontaxane (TAX) tubulin-binding agent with a novel mode of action, was approved in 2011 for the treatment of patients with advanced/metastatic (A/M) BC who have previously received prior chemotherapy. Despite the progress of HER2+ targeted therapies, the most effective treatment strategies are combined anti-HER2 agents with cytotoxic chemotherapy. Also, most HER2+ A/MBC patients will eventually progress because of resistance to anti-HER2 therapies, including Tmab. Hence, more effective and favorable treatments, alone or in combination, are required to treat HER2+ BC.
Materials and Methods
A SLR was conducted adhering to the guidance issued by the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement, and the Cochrane collaboration. Studies that included patients with HER2+ A/MBC on 1L standard of care (SOC), second-line (2L) SOC, and third-line or beyond (3L+) treatments and reporting specific efficacy end points. The searches in the electronic databases were carried out using the Ovid SP platform. To supplement the primary search, searches of conference proceedings published from 2017 to 2021 were performed. All titles and abstracts and full-text papers were reviewed independently by two systematic reviewers. Any disagreements between the two reviewers were resolved with the involvement of a third reviewer or through consensus. Relevant data from the included studies were extracted and the extracted data were validated for accuracy. A formal quality appraisal of the included studies was performed using the Newcastle Ottawa Scale and Cochrane Risk of Bias assessment tool version 2.
Results
2692 citations were screened, and 38 studies were included. Eleven studies were randomized-controlled trials (RCTs; 5 in 1L, 1 in 2L, 5 in 3L+), 6 were non-RCTs (5 in 1L, 1 in 3L+), and 21 were ObSs (13 in 1L, 6 in 2L, 4 in 3L+ [note that studies with subgroups for 1L, 2L, 3L+ are double-counted]). Longer overall survival (OS) was associated with an earlier Tx line (Table). For 3L+ studies that included ERI, ERI, or trastuzumab (Tmab)+ERI led to longer OS than Tx of physician’s choice (median OS, of 11, 10, and 8.9 months, respectively). Progression-free survival was 9 months in Tmab+pertuzumab(Pmab)+ERI, 4 months in Tmab+ERI, and 3.3 months in ERI.
Conclusions
This SLR provides a comprehensive review of the available evidence on the efficacy and safety of treatments in HER2+ patients with A/MBC. However, later lines lack standardization, evidence on the efficacy and safety of treatments in HER2+ patients with A/MBC. However, later lines lack standardization, and conclusions on comparative effectiveness are limited by differing trial designs. Thus, the chance of prolonged survival achieved with less toxic and new agents warrants further research.
AFFILIATIONS:
Kerigo Ndirangu,*1 Rachel Goldgrub,2 Vanita Tongbram,3 Rajee Antony,1 Bagrat Lalayan,1 Joyce O’Shaughnessy,4 Sarah E. Schellhorn5
1Eisai Inc, Nutley, NJ.
2ICON PLC, Vancouver, BC, Canada.
3ICON PLC, New York City, NY.
4Texas Oncology-Baylor Charles A. Sammons Cancer Center, Dallas, TX.
5Yale Cancer Center, Smilow Cancer Hospital, New Haven, CT.
*Kerigo_Ndirangu@eisai.com
