22 Efficacy and Safety of Ribociclib + Nonsteroidal Aromatase Inhibitor in Younger Patients With HR+/HER2− Early Breast Cancer in NATALEE
22 Efficacy and Safety of Ribociclib + Nonsteroidal Aromatase Inhibitor in Younger Patients With HR+/HER2− Early Breast Cancer in NATALEE

Background
NATALEE showed a statistically significant invasive disease-free survival (iDFS) benefit of ribociclib plus nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor (NSAI) vs NSAI (HR, 0.749; 95% CI, 0.628-0.892; P = .0006) in patients with hormone receptor–positive (HR+)/HER2-negative (HER2–) early breast cancer (EBC). We report ribociclib efficacy/safety in patients < 40 vs ≥ 40 years in NATALEE.
Materials and Methods
Patients were treated with ribociclib plus NSAI or NSAI alone. Premenopausal patients received goserelin. Efficacy/safety/patient-reported outcomes were assessed (data cutoff: July 21, 2023; median follow-up, 36.7 months).
Results
Of 5101 patients, 543 (10.6% ribociclib plus NSAI) were
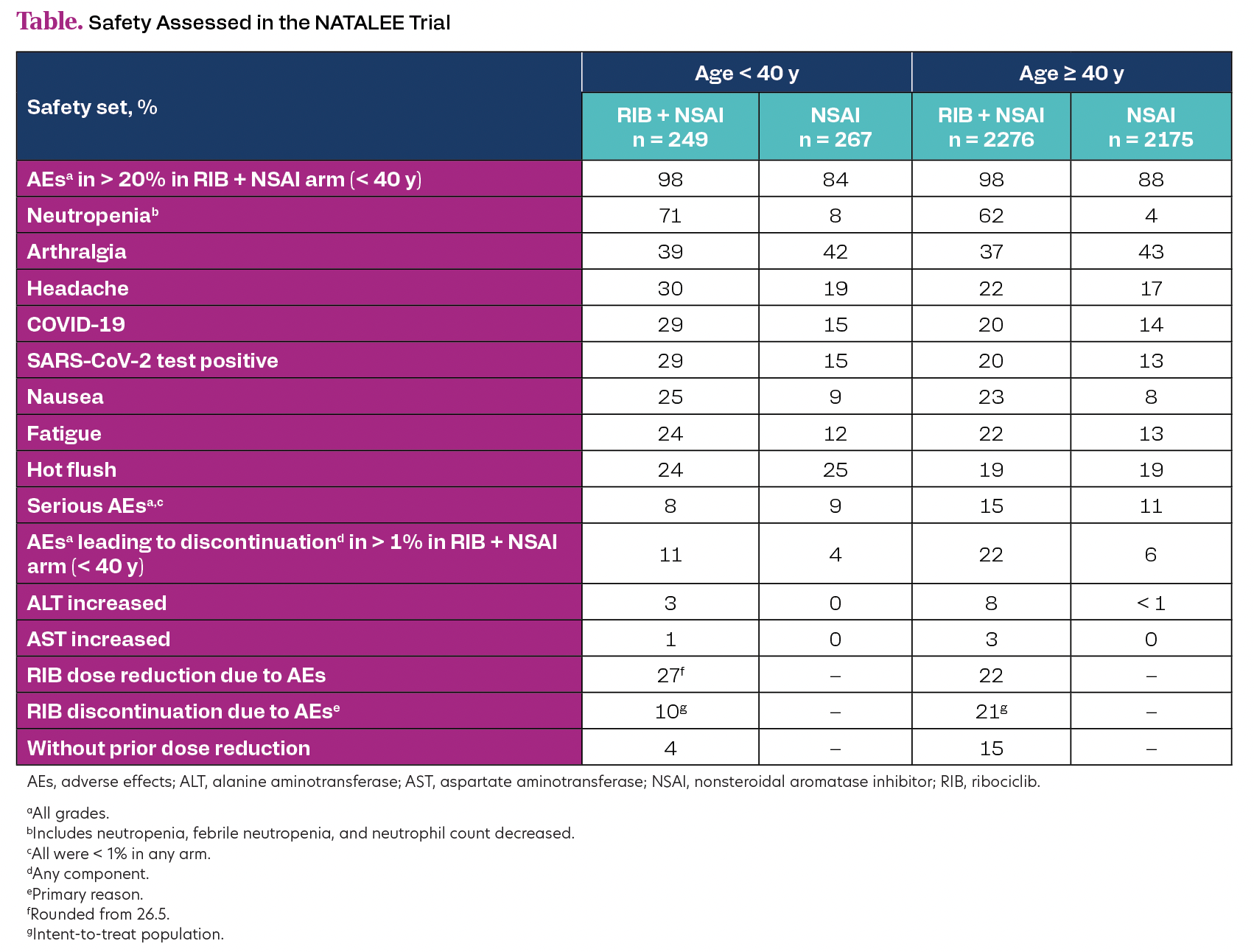
< 40 years (93.9% premenopausal), with 4558 (89.4% ribociclib plus NSAI) ≥ 40 years (38.2% premenopausal). Patients < 40 years were generally at higher risk prior to surgery vs patients ≥ 40 years (neoadjuvant chemotherapy, 61.1% vs 40.5%; G3, 26.5% vs 20.3%; N1-3, 70.0% vs 58.5%). Ribociclib plus NSAI showed iDFS benefit (< 40 years, HR 0.546; 95% CI, 0.321-0.929; ≥ 40 years, HR 0.780; 95% CI, 0.648-0.939), with similar trends for distant recurrence-free, recurrence-free, and distant disease-free survival. 3-year iDFS rates were higher in patients on ribociclib plus NSAI vs NSAI alone among patients < 40 years (90.1% vs 85.0%) and ≥ 40 years (90.7% vs 87.9%). Adverse effect (AE) rates and ribociclib dose reductions/discontinuations are presented in the Table. Global health status and physical functioning scores showed no evidence of difference between arms in patients aged < 40 or ≥ 40 years.
Table. Safety Assessed in the NATALEE Trial
Conclusion
Adjuvant ribociclib plus NSAI showed treatment benefit in patients with HR+/HER2− EBC, including in patients < 40 years, who had more aggressive disease than patients ≥ 40 years. Safety profiles were consistent between age groups, but patients < 40 years were less likely to discontinue ribociclib due to AEs with or without prior dose reduction.
