23 Clinical Outcomes in Patients With HR+/HER2− Early Breast Cancer By Prior Systemic Treatment: A Subgroup Analysis of the NATALEE Trial
23 Clinical Outcomes in Patients With HR+/HER2− Early Breast Cancer By Prior Systemic Treatment: A Subgroup Analysis of the NATALEE Trial

Background
NATALEE met its primary end point with a significant invasive disease-free survival (iDFS) benefit with ribociclib plus nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor (NSAI) vs NSAI in patients with hormone receptor–positive (HR+)/HER2-negative (HER2–) early breast cancer (EBC) that was sustained with additional follow-up (median follow-up, 33.3 months; HR, 0.749). We analyzed iDFS by prior systemic treatment (chemotherapy [CT], endocrine therapy [ET]) in NATALEE using data from the final prespecified iDFS analysis (data cutoff: July 21, 2023).
Materials and Methods
Patients were randomized 1:1 to ribociclib 400 mg/d (3 weeks on/1 week off for 36 months) plus NSAI (≥ 60 months) or NSAI. Men and premenopausal women received goserelin. Eligible patients had anatomic stage IIA (high-risk N0 or N1), IIB, or III EBC, regardless of prior (neo)adjuvant CT. Patients starting ET ≤12 months before randomization were included.
Results
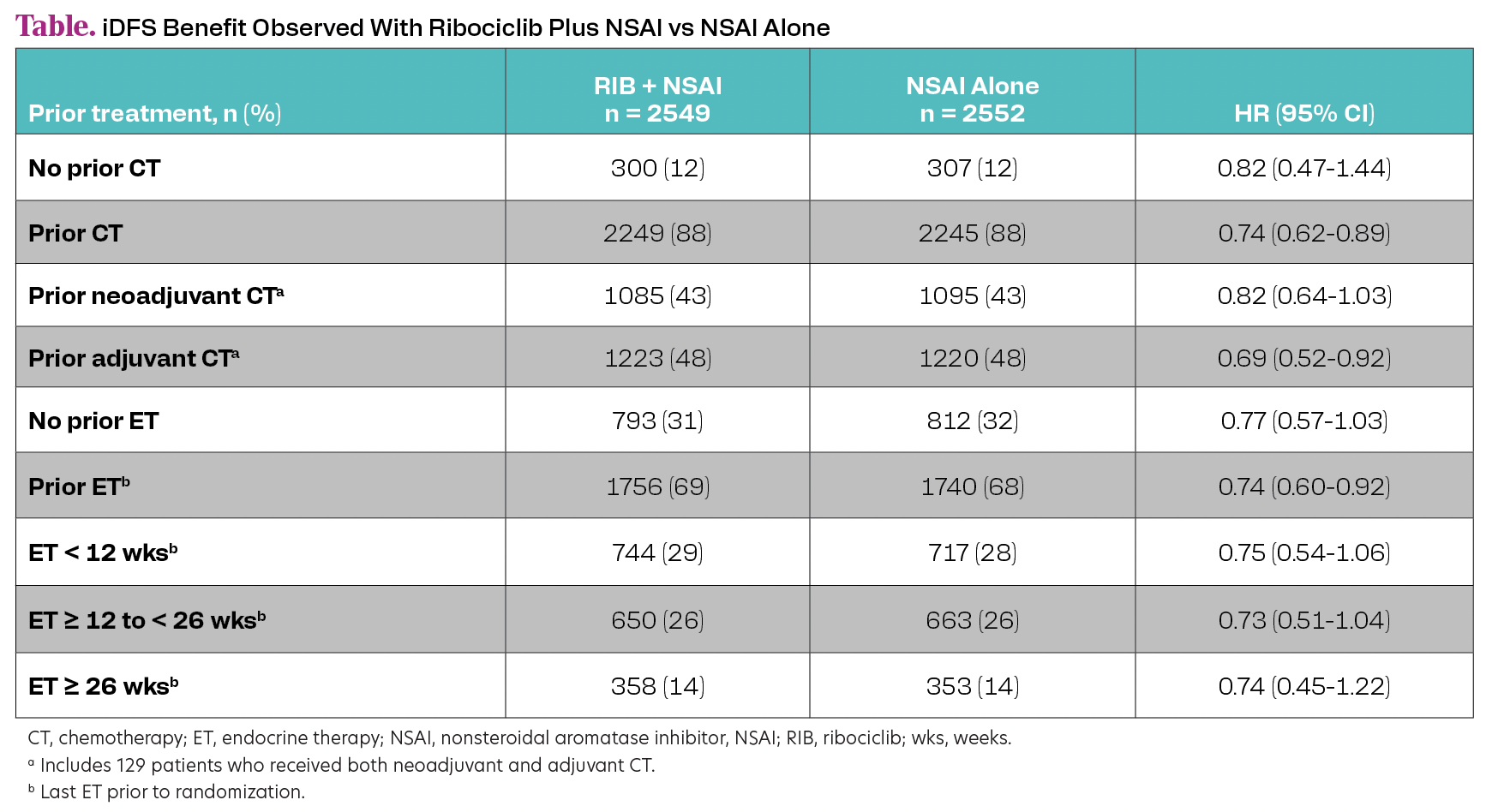
Of 5101 patients, 88% received prior CT, 43% had prior neoadjuvant CT, and 48% had prior adjuvant CT. Of 1432 patients with N0 disease at diagnosis, most had prior CT (78%). Most patients (73%) with prior neoadjuvant CT had stage III disease, while 19% with no prior CT had stage III disease. Overall, 69% of patients received prior ET (median duration of last prior ET was 3.2 months). An iDFS benefit with ribociclib plus NSAI was observed regardless of prior CT or duration of ET (Table).
Conclusion
This subgroup analysis demonstrated an iDFS benefit with ribociclib plus NSAI vs NSAI alone in patients with HR+/HER2− EBC, regardless of duration of prior ET as well as prior (neo)adjuvant CT vs no CT, underlying the potential role of CDK4/6 inhibitors in therapeutic de-escalation of CT in EBC. A majority of patients with N0 disease at diagnosis had received prior (neo)adjuvant CT, highlighting that these patients had a risk of recurrence that was considered high enough to warrant CT.
