29 The Effect of Personality Type on Satisfaction With Information Exchange in Breast Cancer Patients
Background
Type D (distressed) personality is a concept that was coined in the field of medical psychology and is defined as a tendency toward negative affectivity and social inhibition. Previous studies have demonstrated that when compared with other personality types, patients with cancer who have personality Type D experience lower quality of life and mental health status. One theory to explain this difference is that patient dissatisfaction with perceived receipt of information negatively impacts overall well-being. To further evaluate this hypothesis, this study aimed to identify differences in satisfaction with perceived receipt of information among 2 patient populations with a new cancer diagnosis: those with Type D personality and those with non–Type D personality.
Materials and Methods
A prospective survey study included patients diagnosed with breast cancer at a single institution between January 2019 and December 2021. Participants completed a global assessment survey instrument to determine their personality type prior to speaking to their physician. Immediately following their visit, patients then completed the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer – Quality of Life information module (INFO 25). INFO25 is a validated questionnaire composed of 25 questions based on a 4-point Likert scale used to assess patients’ perceived understanding of their diagnosis and treatment. All analyses were conducted using SPSS v27.
Results
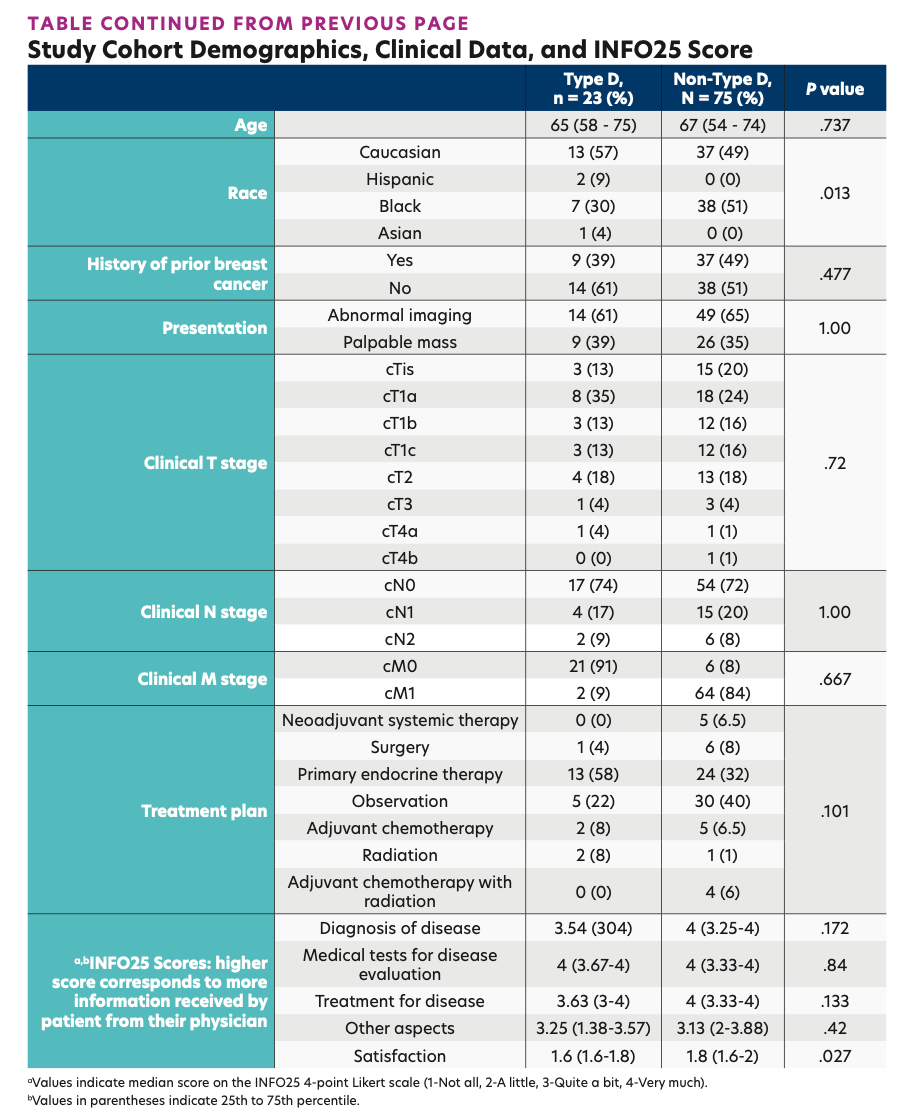
Ninety-eight patients with a diagnosis of breast cancer were enrolled in the study. Presentation, stage, and treatment receipt were similar between both personality groups. Among the 98 patients in the study cohort, 23 (23.5%) patients were Type D. Compared with the non–Type D patients, those with Type D were less satisfied with the provision of information by their physician (1.6 vs 1.8; P <.05). Following their consultation, patients in the Type D arm felt less confident than those in the non–Type D arm, with respect to their level of understanding of “disease diagnosis,’ ‘medical tests,’ and ‘treatment options.”
Conclusions
In this study cohort from a nationally accredited urban cancer center, patients with breast cancer with Type D personality had lower perceived satisfaction with the information provided by their physician. Further studies should investigate methods to optimize information transfer and improve shared decision-making for breast cancer patients with Type D personality.
Study Cohort Demographics, Clinical Data, and INFO25 Score
Author Affiliations:
Vijayashree Murthy,1 Dana Borgen,2 Joshua Feinberg,1 Kristin E. Rojas,3 Vijaya Natarajan,4 Yocasta Mejia,4 Michael Silver,5 Charusheela Andaz,1 Donna-Marie Manasseh1
1Breast Surgery, Department of Surgery, Maimonides Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY
2Rutgers University, The State University of New Jersey, New Brunswick, NJ
3Breast Surgery, Miller School of Medicine, University of Miami, Miami, FL
4Department of Clinical Research, Maimonides Cancer Center, Brooklyn, NY
5Department of Biostatistics, Research Administration, Maimonides Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY
