48 Prevalence of “HER2 Ultra-Low” Among Advanced Breast Cancer Patients With Historical IHC0 Status
48 Prevalence of “HER2 Ultra-Low” Among Advanced Breast Cancer Patients With Historical IHC0 Status

Background
This study aimed to assess the prevalence of “HER2 Ultra-Low” (faint membrane staining in >0 but ≤10% of tumor cells) expression based on re-scored HER2 IHC0 biopsy slides.
Materials and Methods
From all 3 US Mayo Clinic campuses, a total of 300 patients with advanced breast cancer (stages III-IV), and clinically documented HER2 IHC0 status between January 2017 and January 2023, were identified. One biopsy slide per patient (IHC assay: VENTANA Pathway anti-HER2/neu (4B5) rabbit monoclonal primary antibody) was digitized and scanned at 40x magnification. Two Mayo Clinic pathologists independently reported HER2 status and tumor stain percentage for each slide based on 2023 ASCO-CAP guidelines. Patients were considered “HER2 Ultra-Low” if their slide was scored as IHC0 with >0% but ≤10% staining. Cohen’s κ was used to quantify the agreement between pathologists.
Results
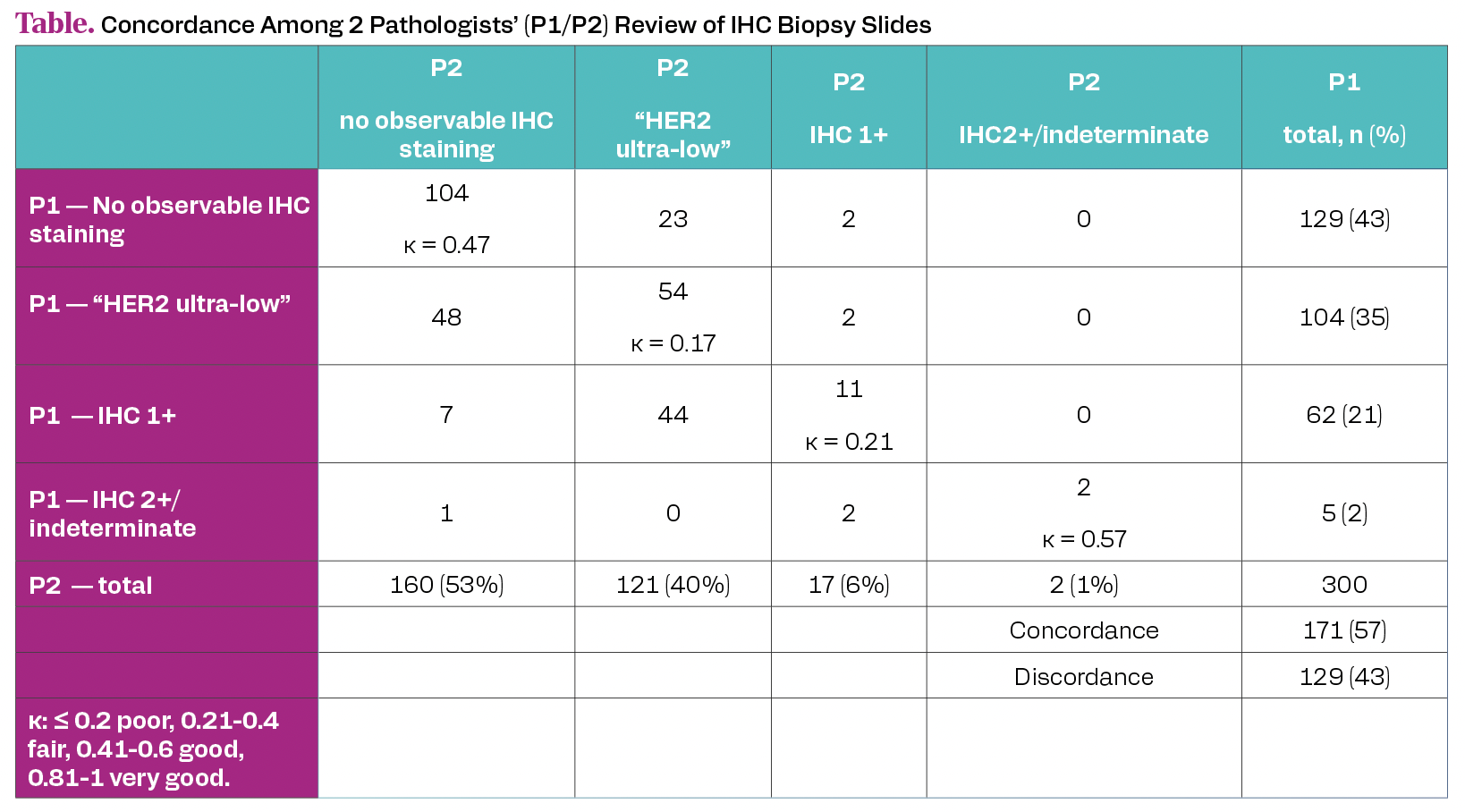
Among 300 re-scored patients (mean age of 57.8 years (SD = 13.5)), 285 patients (95%) remained classified as IHC0 by at least 1 pathologist. Of these (n = 285), 60% (n = 171) were determined as “HER2 Ultra-low” by at least 1 pathologist. The rate of “HER2 Ultra-Low” per pathologist ranged from 43% (n = 121) to 45% (n = 104). The overall inter-pathologist concordance was 57%; patients with no observable HER2 IHC staining accounted for the majority of the concordant patients (Table).
Table. Concordance Among 2 Pathologists’ (P1/P2) Review of IHC Biopsy Slides
Conclusion
About 3 in 5 patients with advanced breast cancer originally classified as HER2 IHC0 met the “HER2 Ultra-Low” criteria by at least 1 pathologist, implying that a significant number of additional patients may benefit from HER2 targeted therapy. The relatively low concordance between HER2 expert pathologists in identifying lower levels of HER2 expression suggests the need for increased precision enabled by digital tools, leveraging artificial intelligence, training for community practice pathologists, and continuing to follow best practice recommendations in determining HER2 IHC status.
