56 Paternal vs Maternal Inheritance of a BRCA Mutation: Is There a Difference in Presentation and Stage of Breast Cancer at Diagnosis?
56 Paternal vs Maternal Inheritance of a BRCA Mutation: Is There a Difference in Presentation and Stage of Breast Cancer at Diagnosis?

Background
BRCA mutations are often associated with a strong family history of breast and/or other cancers, leading to testing and screening before a diagnosis. Paternal family history genetic inheritance may be underrecognized, leading to BRCA testing done only at the time of diagnosis and hence later stage of breast cancer at diagnosis. We investigated the differences in presentation and subsequent management between patients with maternal BRCA (M-BRCA) vs paternal BRCA (P-BRCA) lineage for patients diagnosed with breast cancer. To our knowledge, there are no current studies that exist in the published literature regarding the impact of BRCA lineage on breast cancer stage
and presentation.
Materials and Methods
Retrospective chart review was performed to identify patients with newly diagnosed breast cancer who were also BRCA positive from 2010 to 2022. Pedigree was reviewed, and the lineage of the mutation was assigned as definitively or likely paternal or maternal; we excluded patients whose lineage could not be determined. Comparisons were made between the inheritance groups using a 2-sample independent t-test and binomial regression models.
Results
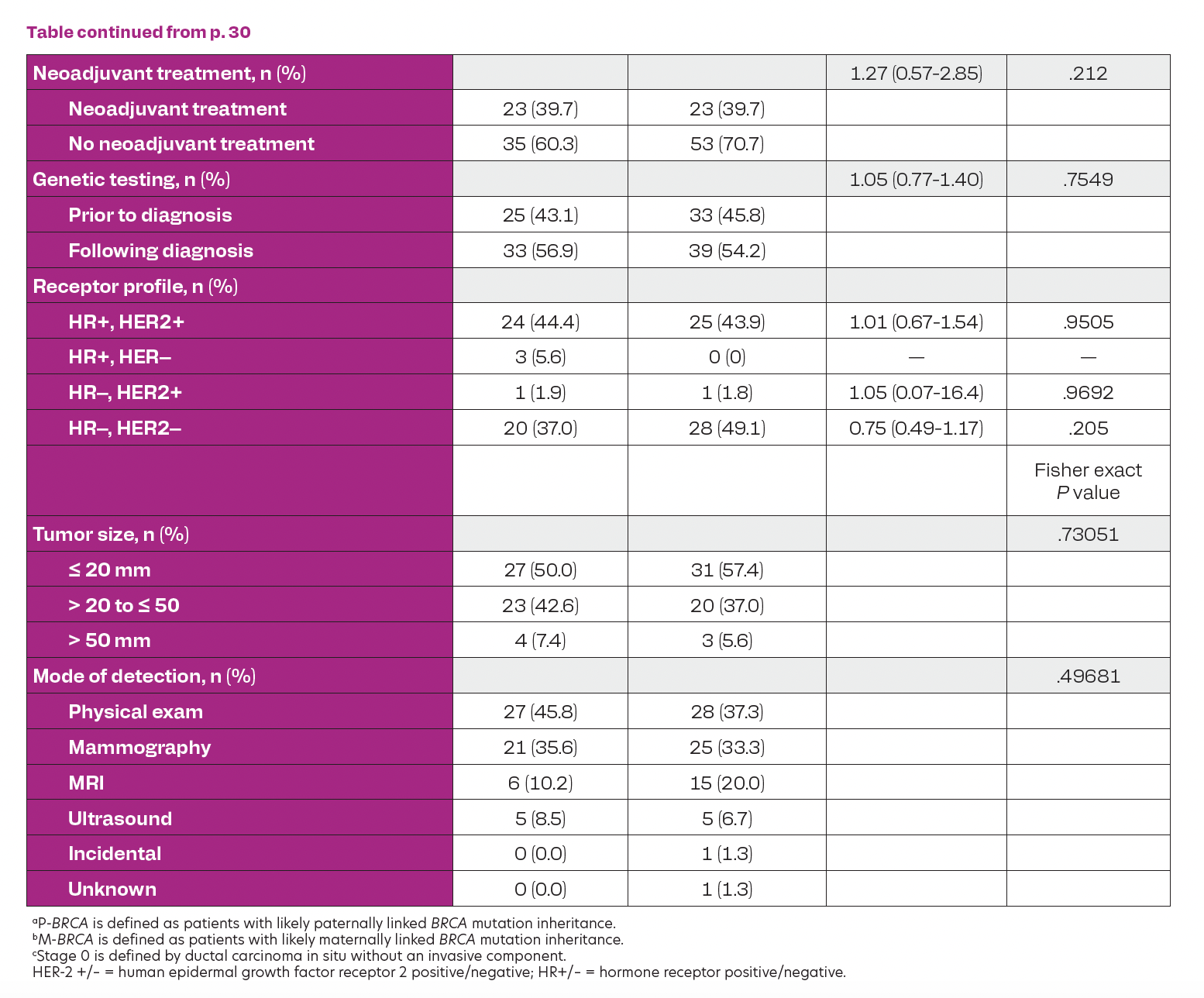
A total of 219 patients who are BRCA-positive with newly diagnosed breast cancer were identified, with 134 patients meeting inclusion criteria where lineage could be determined (Table); 59 (44%) having P-BRCA, with 75 (55%) having M-BRCA. Overall, 111 (83%) had invasive cancer and 23 (17%) had ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). P-BRCA patients were more likely to be diagnosed with invasive cancer, compared with M-BRCA (91.5% vs 76.0%; P = .028), and more likely to be node-positive (23.7% vs 10.7%; P =.0498). There was a trend toward larger tumor size and receipt of neoadjuvant treatment for paternally linked BRCA mutation (23.6 mm vs 20.4 mm and 39.7% vs 29.3%); however, these were not significant. Patients with P-BRCA also tended to be diagnosed with cancer at a younger age compared with M-BRCA, were slightly more likely to be diagnosed with cancer before genetic testing, had fewer MRI-detected cancers and more detected by physical exam, but these were also not statistically significant.
Table. Patient Characteristics of Paternal vs Maternal Inheritance of BRCA Mutation
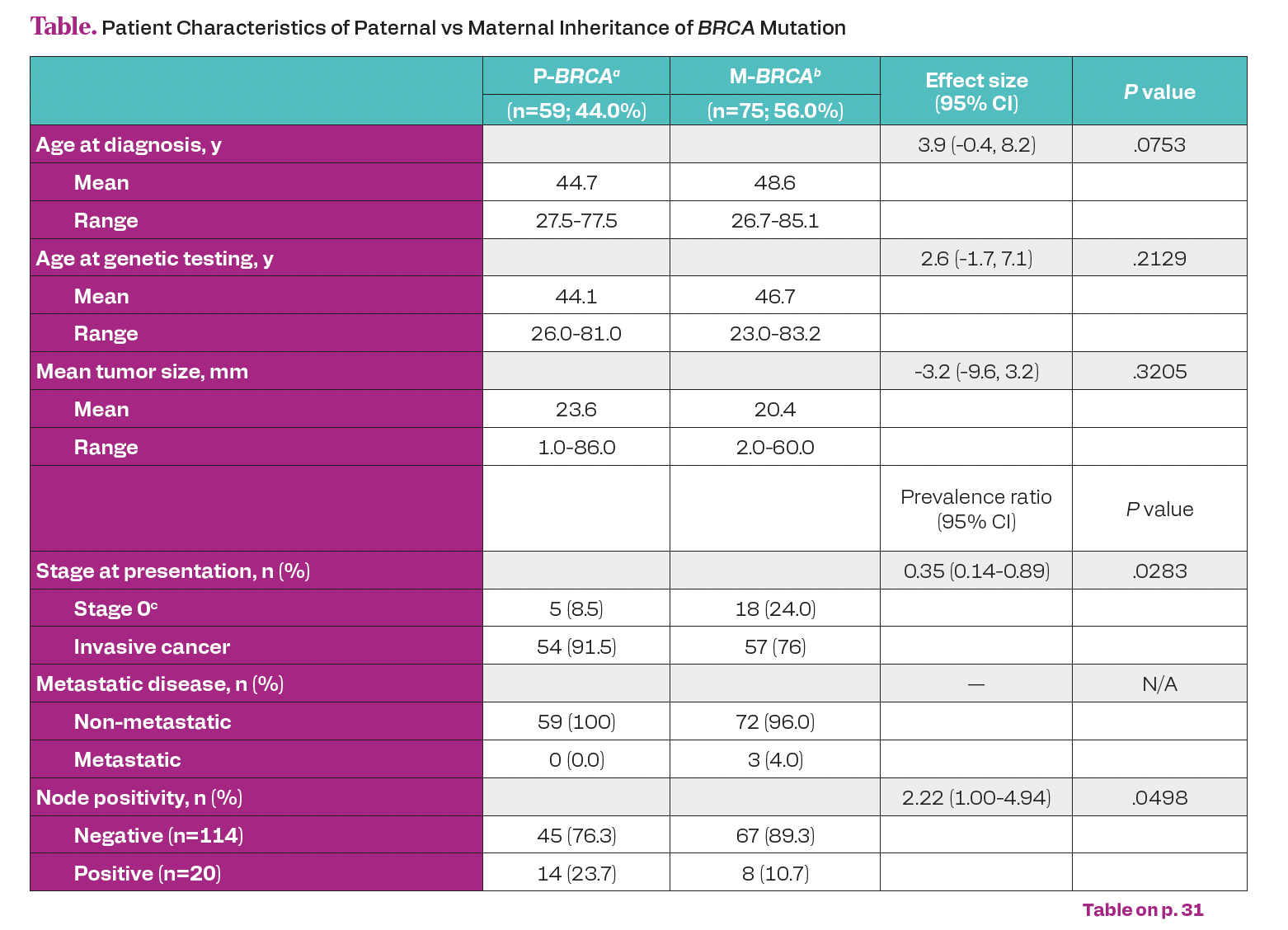
Table. Patient Characteristics of Paternal vs Maternal Inheritance of BRCA Mutation Cont.
Conclusion
Our results support the hypothesis that P-BRCA patients are more likely to present with later stage disease (invasive vs DCIS, node positivity) with a trend toward increased discovery of BRCA-positivity after diagnosis, and by physical exam in lieu of MRI. These data confirm the need for wider testing and awareness related to BRCA transmission through paternal lineage. A larger sample size may show statistical significance among trending variables.
