Cytokines Enhance Effects of Cord Blood Cells Against Breast Cancer
WASHINGTON-Umbilical cord blood cells alone have no cytotoxic properties, but studies show that when activated with interleukin-2 (IL-2), they may have some therapeutic effects against breast cancer, said Shantaram S. Joshi, PhD, associate professor of cell biology and anatomy, University of Nebraska Medical Center.
WASHINGTONUmbilical cord blood cells alone have no cytotoxic properties, but studies show that when activated with interleukin-2 (IL-2), they may have some therapeutic effects against breast cancer, said Shantaram S. Joshi, PhD, associate professor of cell biology and anatomy, University of Nebraska Medical Center.
Studies in Three Cell Lines
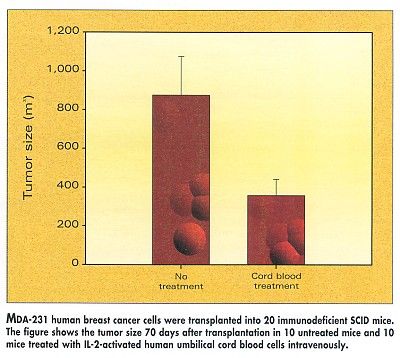
Dr. Joshi, who spoke at the Susan G. Komen Breast Cancer Foundation annual scientific conference, used three cell linesT47D, MCF-7, and MDA-231in his tests of cytokine-activated mononuclear cells from human umbilical cord blood.
Without activation, the cord blood mononuclear cells showed no antitumor activity. But following in vitro activation with IL-2, cord blood mononuclear cells demonstrated significantly increased cytotoxicity against human breast cancer in vitro as well as in vivo against MDA-231 human breast cancer cells grown in SCID mice.
Adding granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and macrophage-colony stimulating factor (M-CSF) to IL-2 increased activation of cytotoxic effector cells and cytotoxicity of cord blood cells against human breast cancer cells, Dr. Joshi said. GM-CSF or M-CSF combined with IL-2 significantly increased the natural-killer cell and dendritic cell population in mononuclear cells derived from cord blood.
"These studies suggest that combination of IL-2 with GM-CSF or M-CSF might be useful in inhibiting the growth of breast cancer in vivo," Dr. Joshi said, "and may lay the foundation for exploring the use of cord blood cells for therapy against breast cancer."