Fixed-Dose UFT/Leucovorin Schedule Promising in Advanced Breast Cancer
MAYWOOD, Illinois-A novel fixed-dose schedule of uracil/tegafur (UFT) plus leucovorin (UFT/LV, also known as Orzel, investigational) achieved significant disease stabilization in advanced breast cancer, according to a phase II multicenter study reported at ASCO (abstract 240).
MAYWOOD, IllinoisA novel fixed-dose schedule of uracil/tegafur (UFT) plus leucovorin (UFT/LV, also known as Orzel, investigational) achieved significant disease stabilization in advanced breast cancer, according to a phase II multicenter study reported at ASCO (abstract 240).
UFT/LV is traditionally given by body surface area (BSA)-based oral dosing two to three times daily for 28 of 35 days. In this trial, a novel twice-daily fixed-dose schedule was tested in patients and found to be active. The study was especially encouraging, the investigators noted, because it showed that a single agent could produce prolonged disease stabilization in heavily pretreated patients.
Lee Schwartzberg, MD, of the West Cancer Clinic, Memphis, Tennessee, was lead author. Principal investigator Kathy Albain, MD, of Loyola University Cardinal Bernardin Cancer Center, Maywood, Illinois, discussed the poster at ASCO.
"Our intention in evaluating this regimen was that it might be more palatable, especially for older women or for women who want a simpler regimen," Dr. Albain said. "We found a response rate that was modest, but the disease stabilization rate was quite high. Almost 30% of patients were free of progression at 6 months."
The study included 86 patients who were given 300 mg/m² UFT and 30 mg leucovorin every 12 hours, Monday through Friday each week. If BSA was 1.5 m2 or less, the UFT dose was reduced to 500 mg/m² for the first 5 weeks of the study. Almost half the patients had received two prior regimens and had three sites of metastasis.
A total of 374 cycles were delivered. The number of days the drugs were withheld due to toxicity was 671 (8%), and the number of days missed for noncompliance was 135 (2%). (See table below for response rates.)
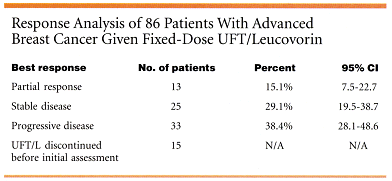
Median duration of response was 427 days (range, 70 to 616), and median time to progression was 80 days. Progression-free survival at 6 months was 27% (95% CI 18% to 37%), and median survival was 431 days.
One drawback of this regimen was the gastrointestinal toxicity, which, Dr. Albain noted, is not unusual for these compounds. Grade 2 diarrhea occurred in 21% of patients and grade 3 in 19%. Grade 2-3 nausea/vomiting occurred in approximately 30%. Other toxicities were infrequent. "Our recommendation, especially if this regimen is taken into the adjuvant setting, is to give the usual premedications for chemotherapy-induced nausea, such as prochlorperazine. Early use of antidiarrheals is also recommended. This most likely would ameliorate the GI toxicity," she said.