Management of Colorectal Cancer in Older Patients
An increasing body of evidence suggests that geriatric patients can benefit from and tolerate standard chemotherapy similarly to younger patients in the settings of both early- and advanced-stage colorectal cancer. Assessment of this unique population requires more comprehensive evaluation in addition to routine history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Specific considerations of their physiologic functional changes will help physicians better manage these patients. Ongoing studies are now designed to better understand the decision-making process, safety profile, and efficacy of various treatment regimens in geriatric patients.
An increasing body of evidence suggests that geriatric patients can benefit from and tolerate standard chemotherapy similarly to younger patients in the settings of both early- and advanced-stage colorectal cancer. Assessment of this unique population requires more comprehensive evaluation in addition to routine history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Specific considerations of their physiologic functional changes will help physicians better manage these patients. Ongoing studies are now designed to better understand the decision-making process, safety profile, and efficacy of various treatment regimens in geriatric patients.
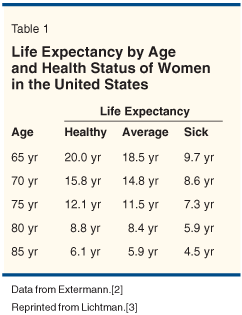
The population of patients over 65 years old is rapidly expanding due to a significantly improving life expectancy globally. Since cancer disproportionately strikes this age group, oncologists, whether community-based or academically oriented, will face a growing population of geriatric cancer patients. Among those affected, colorectal cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related death, with a median age at diagnosis of approximately 72 years.[1] Life expectancy among older individuals is considerable, as shown for US women in Table 1.[2,3] A 75-year-old woman, for example, has a life expectancy of 12 years if she is healthy and would have a life expectancy of 7 years even if she had significant illness. Therefore, issues concerning adjuvant therapy, prolongation of the disease-free interval, and chronic toxicity are also important for the elderly.
Major concerns in the care of geriatric cancer patients include:
(1) Comorbidities. This population is extremely heterogeneous. Patients can vary from very fit to not being able to live independently due to comorbidities.[4]
(2) Aging process. Aging is a gradual diminution in physiologic reserve or functional capacity over time.[5] Because of this process, geriatric cancer patients with significant comorbidity may not tolerate chemotherapy as well as their younger counterparts. That said, older fit patients usually do not experience increased toxicity.
(3) Limited clinical trial data for geriatric cancer patients.[6] Despite rapid progression in the treatment of colorectal cancer in recent years, dedicated clinical trials for geriatric cancer patients are limited. The median age for all landmark studies of clinical treatment for various stages of colorectal cancer is younger than 65 years of age. Many reports have confirmed the fact that smaller proportions of older cancer patients are referred for clinical trials.[7]
In this article, we will review aspects of the treatment of colon cancer in geriatric cancer patients based on published clinical data specific for geriatric patients.
Physiologic Aspects of Aging
Before discussing chemotherapeutic options, the first step in evaluating older colorectal cancer patients is to better understand the physiologic aging process and its impact on chemotherapy and its toxicity. This diminution of functional reserve or capacity assumes great clinical significance when the organ system is being challenged by cancer and its treatment. The loss of functional reserve is often quite variable during aging. It is also difficult to predict the individual patient's tolerance of cancer treatment. Physiologic changes in functional reserve affect not only the choice of chemotherapeutic agent, but more importantly, the tolerance of side effects of therapy. These physiologic changes can involve all systems and organs (Tables 2 and 3).[8]


Toxicities related to chemotherapy for colorectal cancer mostly affect the gastrointestinal tract, renal function, and peripheral nervous systems. Gastrointestinal mucosal protective mechanisms and the ability for self-repair decrease with age.[9] The secretion of bicarbonate is decreased, with subsequent decreased buffer function.[10] Due to renal function changes and the effect of drug toxicity in the kidneys, geriatric cancer patients are at higher risk of volume depletion and prerenal azotemia.[11,12] Clearly, the treatment of geriatric patients with chemotherapy is complex and unpredictable.
In evaluating renal function, 24-hour urine assays can be used as a way of estimating creatinine clearance. However, this approach is often misleading, as serum creatinine does not reliably reflect renal function.[13,14] The widely used Cockcroft-Gault equation has been shown to underestimate creatinine clearance in geriatric patients because reduced muscle use may lead to a decrease of creatinine production.[15] This equation was derived from a dataset of 249 men, all of whom were inpatients at a veterans' hospital. The patients ranged in age from 18 to 92 (mean age: 57 years) and 59 (24%) were > 70 years old. The formula was derived using 24-hour creatinine clearance values as the standard. Although no females were used in the dataset, the Cockroft-Gault method assumes a reduction in glomerular filtration rate of 15% for this population.[16] Various formulae have been proposed as potential alternatives.[17,18]
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials provide physicians and patients invaluable information regarding disease processes and outcomes. One study found that while 63% of people in the general population age 65 or older had cancer, only 25% of patients in that age group were represented in clinical trials.[7] One of the reasons for this may be that physicians are not recommending clinical trials to older patients. In fact, studies have reported that up to 50% of physicians did not offer clinical trials to their elderly patients, based on age alone.[19]
A study of women with breast cancer revealed that while physicians asked 51% of patients younger than 65 years to participate in clinical trials, only 35% of those over 65 were offered the opportunity.[20] In most cases, physician bias stemmed from the assumption that older people cannot tolerate chemotherapy or that the risks of therapy are not worth the benefits. This leads to poor representation of elderly patients in clinical trials, which unfortunately fails to adequately represent the population developing cancer. When the number of patients who entered clinical trials was compared with the estimated number of patients with cancer in each decade of age, the underrepresentation was striking. More than half of children aged 5 to 9 years are accrued to National Cancer Institute (NCI)-sponsored clinical trials, compared with less than 1% of adults aged 75 to 79 years. Among adults, those 80 years of age or older are least likely to be enrolled.
A variety of factors have been proposed as potential explanations for the lower trial accrual associated with advancing age. These include patient and physician expectations, poor social support, other comorbidities, and the unwillingness of third parties to pay for clinical trials.[20,21] For example, the recently published adjuvant trial of oxaliplatin (Eloxatin), leucovorin, and fluorouracil (5âFU) had patients with a median age of 61 years, which is more than a decade younger than the median age of people with the disease in the general population. This highlights the information gap facing the practicing clinician.[22]
Use of Adjuvant Therapy in the Elderly
The need for postsurgical treatment is dictated primarily by the stage of the cancer. For patients with node-positive (stage III) colorectal cancer, adjuvant treatment reduces the risk of death by up to one-third, compared with surgery alone.[23-25] The NCI states that patients with stage III disease who are unable to enter a clinical trial should be offered adjuvant therapy unless there are medical or psychosocial contraindications.[26] Unfortunately, older patients with stage III colon cancer are offered and receive adjuvant chemotherapy less frequently than younger patients.[27-30] According to the NCI's Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) program, which includes data on approximately 11% of the population, only 48% of patients 65 to 74 years old, and 24% of those 80 to 84 years old received adjuvant therapy for node-positive colorectal cancer.[29]
Studies have confirmed that age at diagnosis directly correlates with the use of adjuvant chemotherapy. Age at diagnosis is the strongest determinant of adjuvant chemotherapy for stage III colon cancer: 78% of patients aged 65-69 years, 74% of those aged 70-74 years, 58% of those aged 75-79 years, 34% of those aged 80-84 years, and 11% of those aged 85-89 years received postoperative chemotherapy. The association between age and chemotherapy use remained statistically significant after adjustments for all variables in a multiple logistic regression model. Treatment rates decline dramatically with chronologic age; because patients in their 70s and even 80s have a reasonable life expectancy, further efforts are needed to ensure that elderly patients have the opportunity to make informed decisions regarding a potentially curative therapy.[27,31]
Benefit in Older Patients
Clear evidence demonstrates the effectiveness of adjuvant chemotherapy for resected colorectal cancer in geriatric patients. The combination of leucovorin and 5-FU has been established as a standard, effective adjuvant regimen for limited colorectal cancer.[32] Sargent et al performed a pooled analysis of data from randomized trials comparing adjuvant 5-FU-based regimens with no adjuvant chemotherapy in elderly patients with resected stage II/III colon cancer.[33] This analysis of over 3,000 patients (1,446 with stage II and 1,905 with stage III colon cancer) showed: (1) There is no significant cross-action between age and treatment effect for overall survival and freedom from tumor recurrence. (2) Elderly patients have about the same level of side effects, including nausea, vomiting, stomatitis, and diarrhea, compared to younger patients, with the exception of a trend toward a higher incidence of leukopenia.
A study by Jessup et al in 85,934 patients with stage III colon cancer in the National Cancer Data Base between 1990 and 2002 revealed similar findings.[34] A total of 23,507 patients aged 70 years and older were identified. The 5-year survival rate of this group on adjuvant chemotherapy is similar to that of patients in the younger age groups. The 5-year survival of patients 80 years and above treated with adjuvant chemotherapy was 19% better than patients 80 years or older who received surgery alone, while the youngest cohort of patients had only a 10% increase in 5-year survival with surgery plus adjuvant chemotherapy, compared to surgery alone.
In 2004, Folprecht et al published a pooled retrospective analysis of 3,825 patients with metastatic colorectal cancer who received a 5-FU-based regimen in 22 European trials.[35] A total of 929 patients aged 70 years and older were identified. Infusional 5-FU was associated with significantly increased response, overall survival, and progression-free survival rates compared to bolus 5-FU regimens in all patients. More importantly, the response rate was similar when comparing patients older than 70 years to patients aged 70 years or younger.
As a result of the better understanding in the treatment of geriatric colorectal cancer patients, there have been increasing worldwide reports of offering and treating this population with adjuvant chemotherapy.[36]
Adjuvant Regimens
• 5-FU-Based Regimens-Several regimens have demonstrated efficacy for adjuvant colorectal cancer treatment. These regimens include 5-FU and leucovorin (weekly Roswell Park regimen or monthly Mayo Clinic regimen).[32] The use of 5-FU with or without leucovorin has been the standard adjuvant treatment approach for over 30 years. In recent years, oxaliplatin has been added, demonstrating substantial improvements in disease-free and overall survival.[22]
The antimetabolite 5-FU has demonstrated highly variable interpatient pharmacokinetics. Although age has been shown to have no effect on the clearance of 5-FU, gender does appear to a play a role. Women clear 5-FU at significantly lower rates than men, correlating with approximately 15% lower dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase activity. This correlates with the clinical observation that women have increased toxicity, specifically stomatitis and leukopenia.[37]
5-FU has been infused via numerous schedules with little difference in efficacy. The drug has also shown variability in the degree of toxicity, mostly noted in older patients. In a trial using 5-FU and leucovorin in a monthly cycle (Mayo Clinic regimen), patients over 70 years of age experienced more grade 3/4 mucositis than the younger group, and the regimen proved less tolerable, particularly for the elderly, than the weekly Roswell Park schedule. However, a retrospective series revealed that elderly patients experienced benefits and toxicities similar to what is seen in younger patients when given infusional 5-FU vs bolus therapy.[35] In both age groups, infusional 5-FU resulted in significantly increased response, overall survival, and progression-free survival rates, compared to results with bolus 5-FU. From these reports, it would seem that increased toxicity in the elderly is dependent on schedule, gender, and performance status.
Of note, the Quick And Simple And Reliable (QUASAR) investigators demonstrated efficacious results using an adjuvant bolus regimen with a lower leucovorin dose in a somewhat older patient population (36% over 70 years).[38]
• Capecitabine-Capecitabine (Xeloda) therapy has been compared to an intravenous fluoropyrimidine-based regimen. The X-ACT trial demonstrated a similar, favorable safety profile for both regimens in patients under age 65 as well as in those aged 65 and older.[39,40] The superior relapse-free survival rate and safety profile led to the US Food and Drug Administration approval of capecitabine for the treatment of stage III colon cancer.
Diaz-Rubio et al performed a retrospective analysis on data from the geriatric patients (age 70 years and older) in the X-ACT trial.[41] The improved safety profile of capecitabine was maintained in this patient population. Age, sex, body surface area, and hepatic dysfunction did not significantly affect the drug's pharmacology. This drug is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment and should be used with caution in patients with renal insufficiency. However, the toxicity profile of capecitabine differed in several important respects from that of intravenous bolus 5-FU/leucovorin (Mayo regimen). Capecitabine was associated with a substantially lower incidence of diarrhea, stomatitis, nausea, and alopecia. Grade 3/4 stomatitis and neutropenic sepsis, as a consequence of rare neutropenia, were significantly less common among patients treated with capecitabine. In addition, there were significantly fewer hospitalizations for the treatment of adverse events with capecitabine. Therefore, capecitabine demonstrated clinically meaningful benefits over the monthly bolus 5-FU/leucovorin in terms of tolerability.
• FOLFOX-The MOSAIC trial was a large, randomized, multicenter, multinational phase III study, the primary end point of which was to demonstrate a 25% decrease in the risk of tumor recurrence at 3 years among patients with stage II/III colon cancer receiving infusional 5-FU/leucovorin plus oxaliplatin.[22] Over 2,000 patients with completely resected stage II/III colorectal cancer were randomly assigned to receive bolus followed by infusional 5-FU/leucovorin (de Gramont regimen) or infusional 5-FU/leucovorin plus oxaliplatin (FOLFOX) bimonthly for 12 cycles. The median age was 60-61 years, and approximately one-third of patients were over age 65. Males slightly outnumbered females, and all patients had a good performance status.
Results from this trial revealed low (0.5%) mortality in both the FOLFOX and 5-FU/leucovorin arms. Disease-free survival was significantly improved in the FOLFOX arm, with 78.2% of patients surviving without recurrence at 3 years (95% confidence interval [CI] = 75.6%-80.7%), compared with 72.9% of those in the 5-FU/leucovorin group (95% CI = 70.2%-75.7%), which corresponds to a 23% reduction in the risk of relapse (P = .002). Increases in grade 1-3 neuropathy were reported in the FOLFOX arm, but after 1 year, the incidence decreased to 1.1%. Thus, the FOLFOX regimen should be considered in older patients with adequate performance and functional status.
Can geriatric patients with resected colorectal cancer tolerate 6 months of FOLFOX? Sargent et al[42] presented a meta-analysis of FOLFOX trials and analyzed the data by patient age. Overall, the analysis involved 3,700 patients in four trials, with 493 patients aged 70 and older. The analysis showed no difference in survival, toxicity, or dose intensity by age, a finding similar to the results of studies in advanced disease.
Advanced Colorectal Cancer
Despite the complications attending the treatment of older patients, evidence indicates that they benefit from standard treatments for colorectal cancer similarly to younger patients.[44] Although certain caveats apply to the treatment of older patients, effective therapies should not be withheld from this population simply on the basis of age. Chemotherapy for metastatic colorectal cancer has changed rapidly in the past 5 years. Until recently, 5-FU/leucovorin as a bolus regimen was the standard of care. Current standard first-line regimens for nonelderly stage IV colorectal cancer patients with good performance status are FOLFOX and/or FOLFIRI (irinotecan [Camptosar], leucovorin, 5-FU), with or without bevacizumab (Avastin).[45] Evidence suggests that these regimens are safe and efficacious for the geriatric patient population.
Irinotecan
In 1999, a multicenter study reported by Rothenberg et al showed increased toxicity in elderly patients more than 65 years old who have been treated with weekly irinotecan. This is reflected in the package insert, where dose modification is recommended for patients older than 70 years.[46] However, analysis of data from the published phase III trial by Douillard et al has indicated that age is not an adverse prognostic factor for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer treated with irinotecan in combination with 5-FU.[47]
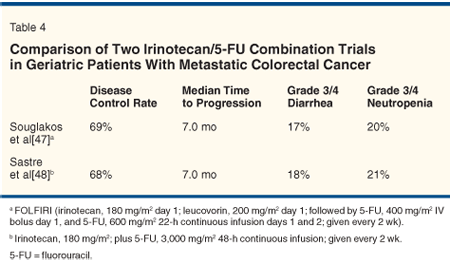
In 2005, Souglakos et al reported a phase II trial of FOLFIRI in patients older than 70 years.[48] The overall response rate was 33.3%, with 36% of patients showing stable disease, and the total disease control rate was 69%. The median time to disease progression was 7.0 months. Grade 3/4 neutropenia has been observed in 20% of patients, and grade 3/4 diarrhea in 17% patients.
Similar data were seen in the results published by Sastre et al in 2005, evaluating efficacy and safety profiles in 86 patients over 72 years of age.[49] These patients were treated with irinotecan at 180 mg/m2 followed by 5-FU at 3,000 mg/m2 in a 48-hour continuous infusion. The two drugs were given every 2 weeks. A total of 68% of patients obtained disease control, and the median duration of response was 7.0 months (95% CI = 4.2-9.9 months). Grade 3/4 neutropenia and diarrhea were seen in 21% and 18% of patients, respectively. Two deaths were reported; one died of grade 4 diarrhea resulting in renal failure, and the other died of intestinal hemorrhage. The data from these two trials suggest that irinotecan in combination with 5-FU may be a feasible regimen for geriatric patients (Table 4). Diarrhea remains the most threatening side effect.
In the original Saltz et al trial of bolus ILF (irinotecan, leucovorin, 5-FU), age was not a factor in either excess toxicity or poor outcome.[50] However, in practice, most clinicians use a modified Saltz regimen (2 weeks on and 1 week off) that appears to be better tolerated than the original 4 weeks on and 2 weeks off schedule. Special precautions should be taken when irinotecan is used in patients with hepatic or renal dysfunction.[51] The early institution of aggressive supportive measures to treat diarrhea and neutropenia may help decrease mortality from complications associated with irinotecan.
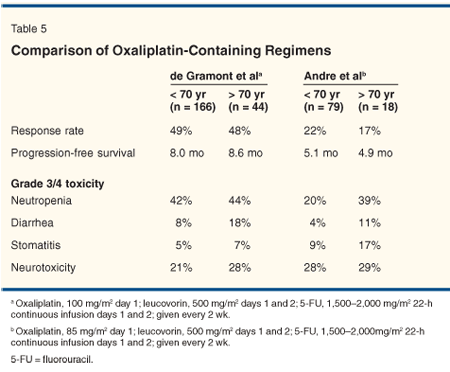
• Oxaliplatin Combinations-Several publications have analyzed oxaliplatin-containing regimens in the forms of FOLFOX and XELOX (oxaliplatin plus capecitabine) for geriatric patients with advanced colorectal cancer.[52] Subset analysis has indicated that age is not an independent factor for efficacy and that geriatric patients may benefit from oxaliplatin regimens with comparable rates of disease control, progression-free survival, median survival, and neurotoxicity.[53,54] However, elderly patients indeed have a higher incidence of neutropenia and gastrointestinal toxicities including mucositis and diarrhea (Table 5). All of these studies are based on subset analyses; therefore, the actual toxicity profile in geriatric patients remains unknown.
In 2005, Mattioli et al reported a study of bifractionated oxaliplatin combined with 5-FU/leucovorin in patients 70 years of age or older, in an attempt to reduce neuropathy.[55] Patients were given oxaliplatin, 45 mg/m2; leucovorin, 200 mg/m2; 5-FU, 400 mg/m2 and 5-FU 600 mg/m2 continuous infusion for 22 hours on days 1 and 2. The overall response rate was 51% (95% CI = 42%-63%) and overall tumor control rate was 76%. The median duration of response was 9 months. Only grade 3 neurotoxicity was seen (6%), and grade 3/4 diarrhea occurred in 10.2% of patients. Most importantly, activities of daily living (ADL) and instrumental activities of daily living (IADL) scores remained stable through 12 cycles of treatment.
Comella et al reported their experience with the combination of oxaliplatin and capecitabine in geriatric patients.[56] Oxaliplatin was given every three weeks, with the dose titrated from 85 mg/m2 to 130 mg/m2, and capecitabine was titrated from 1,000 mg/m2 to 1,250 mg/m2 twice daily from day 2 to day 15. The overall response rate was 41%, and no grade 4 diarrhea or neutropenia have been reported. The frequency of grade 3 diarrhea and neutropenia was 16% and 7%, respectively. However, 7% of patients reported grade 4 hand-foot syndrome.
Twelves et al also reported their results in using XELOX (capecitabine, 1,000 mg/m2 twice daily from day 1 evening to day 15 morning, after oxaliplatin, 130 mg/m2 on day 1) in patients aged 65 years and older.[57] The reported response rate was 52%, and no clinically relevant difference between younger and older patients was observed. Upfront dose reduction is not required when XELOX is prescribed in patients who are 65 years and older, in light of several reports on the combination's safety profile and efficacy.[58,59]
Oh et al attempted to reduce toxicity in geriatric patients by using a mini-FOLFOX regimen, and no grade 4 toxicity was reported.[60] It remains to be seen whether this is an acceptable alternative regimen for geriatric patients.
• Capecitabine-Feliu et al reported their study of capecitabine as a single agent in patients older than 70 years.[61] Capecitabine dosing was based on the patient's creatinine clearance as calculated with the Cockcroft-Gault formula. Patients with creatinine clearance rates above 50 mL/min received capecitabine, 1,250 mg/m2 twice daily, 2 weeks on and 1 week off. For patients with creatinine clearance rates between 30 and 50 mL/min, 950 mg/m2 of capecitabine were given by the same schedule. Capecitabine was withheld if creatinine clearance was less than 30 mL/min. The reported overall response rate was 24% (95%CI = 15%-41%), and the disease control rate was 67%.
Biologic Therapy
• Bevacizumab-Bevacizumab (Avastin) is a humanized monoclonal antibody against vascular endothelial growth factor. In a randomized study, bevacizumab was combined with bolus ILF. Patients receiving the antibody had a 5-month survival advantage over those who did not. Based on these data, bevacizumab has been approved for use in metastatic colorectal cancer in combination with fluorouracil-based chemotherapy. Fit elderly patients should be offered these treatments with close monitoring for hypertension, proteinuria, thromboembolic complications, bleeding, perforation of the gastrointestinal tract, and wound healing.[62]
Bevacizumab has also been combined with leucovorin/5-FU in elderly patients and FOLFOX with proven efficacy.[63-66] The main reported side effects include hypertension, epistaxis, arterial thrombosis, proteinuria, and gastrointestinal perforation. However, patients with active coronary artery and vascular disease were excluded from the bevacizumab trials.[62,66] Many geriatric patients have controlled hypertension and coronary artery disease as well as a history of transient ischemic attacks and stroke. It is not clear whether it is safe to administer bevacizumab to these patients. Extensive discussion about risk factors for severe side effects will help physicians, patients, and families assess the risk-benefit ratio.
• Cetuximab-The chimeric monoclonal antibody cetuximab (Erbitux) has been approved for use in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-expressing metastatic colorectal cancer, either as a single agent or in combination with irinotecan in patients refractory to irinotecan-based therapy, and as a single agent in patients who are intolerant to irinotecan-based therapy.[67] EGFR is overexpressed in the majority of patients with colorectal cancer, and in some studies has been correlated with poorer outcome.[68-70]
Cetuximab is relatively well tolerated, and the most common side effects are skin rash, diarrhea, and allergy. Given the side-effect profile of cetuximab, it appears that geriatric patients can tolerate it well with no significant life-threatening toxicity. The combination of irinotecan and cetuximab remains an option for geriatric patients with irinotecan-refractory disease. Although cetuximab has some efficacy as a single agent, it remains to be seen whether it is cost-effective in geriatric patients who have significant comorbidity and poor performance status and who otherwise cannot tolerate combined chemotherapy.
Multifactorial Decisions in Geriatric Patients With Colorectal Cancer
We need to remind ourselves that the geriatric patients who were included in the trials discussed above are the "good" and "fit" ones with good Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status. As mentioned, the geriatric patient population is a very heterogeneous group. Therefore, we cannot just blindly offer clinical trial regimens to every patient that walks into our office. When managing a geriatric patient with colorectal cancer, in either adjuvant or palliative settings, multiple factors unique to the geriatric population should be considered before a final decision on treatment options is made:
(1) Comprehensive geriatric assessment (CGA). This evaluation comprises ADL/IADL scales, MMSE assessment, and the geriatric depression scale (GDS), along with physical examination and laboratory tests. This comprehensive process helps identify geriatric patients who are "fit" and who should be offered standard chemotherapy.[71] Simplified assessments are currently under study.[72]
(2) Comorbidities and associated polypharmacy. Geriatric patients may be seeing physicians from different disciplines for their problems and complaints. This often confusing situation frequently leads to polypharmacy, especially when the treating physicians do not communicate with each other. Side effects of nonchemotherapy drugs can magnify patients' side effects from chemotherapy. Careful reviews of their medications before and during treatment and good communication among treating physicians can help avoid complications from drug interactions. Patients should also be educated to keep an accurate list of their medications and dosage at all times.
(3) Life expectancy. Before adjuvant or palliative chemotherapy is offered, physicians should assess a patient's non-cancer-related life expectancy. Chemotherapy will only be worthwhile if the projected cancer survival is meaningfully longer than the patient's noncancer life expectancy. Current statistics indicate that the 5-year survival rate for average 80 year olds in the United States is about 70%, with total remaining life expectancy being 7.5 years for men and 9.1 years for women.
(4) Patient's social support status and ethnic background. Patients with limited or no social and family support are more vulnerable to side effects of chemotherapy. On the other hand, patients with major family involvement in their lives may make treatment decisions based on family members' pressure or instruction. Some geriatric patients depend solely on their physician's guidance and become confused when data are presented for decision-making.
Conclusions
Age should not prompt a "knee-jerk" decision to exclude geriatric patients with colorectal cancer from appropriate treatment. Comprehensive evaluation of patients belonging to this unique yet heterogeneous population is the first crucial step in management. Patients with good physical and mental functioning and reasonable life expectancy should receive the full range of standard therapy with no upfront dose reduction. Patients who have significant comorbidities and limited life expectancy should be offered either best supportive care or alternative better-tolerated regimens.
Disclosures:
The author(s) have no significant financial interest or other relationship with the manufacturers of any products or providers of any service mentioned in this article.
References:
1. National Cancer Institute: SEER cancer statistics review, 1975-2001. Available at
http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2001/results_merged/topic_med_age.pdf. Accessed May 4, 2006.
2. Extermann M, Balducci L, Lyman GH: What threshold for adjuvant therapy in older breast cancer patients? J Clin Oncol 18:1709-1717, 2000.
3. Lichtman SM: Management of advanced colorectal cancer in older patients. Oncology (Williston Park) 19:597-602, 2005.
4. Extermann M: Measurement and impact of comorbidity in older cancer patients. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 35:181-200, 2000.
5. Lichtman SM: Physiological aspects of aging. Implications for the treatment of cancer. Drugs Aging 7:212-225, 1995.
6. Talarico L, Chen G, Pazdur R: Enrollment of elderly patients in clinical trials for cancer drug registration: A 7-year experience by the US Food and Drug Administration. J Clin Oncol 22:4626-4631, 2004.
7. Hutchins LF, Unger JM, Crowley JJ, et al: Underrepresentation of patients 65 years of age or older in cancer-treatment trials. N Engl J Med 341:2061-2067, 1999.
8. Sawhney R, Sehl M, Naeim A: Physiologic aspects of aging: Impact on cancer management and decision making, Part I. Cancer J 11:449-460, 2005.
9. Newton JL: Changes in upper gastrointestinal physiology with age. Mech Ageing Dev 125:867-870, 2004.
10. Guslandi M, Pellegrini A, Sorghi M: Gastric mucosal defences in the elderly. Gerontology 45:206-208, 1999.
11. Kaplan C, Pasternack B, Shah H, et al: Age-related incidence of sclerotic glomeruli in human kidneys. Am J Pathol 80:227-234, 1975.
12. Adachi T, Kawamura M, Owada M, et al: Effect of age on renal functional and orthostatic vascular response in healthy men. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 28:877-880, 2001.
13. Swedko PJ, Clark HD, Paramsothy K, et al: Serum creatinine is an inadequate screening test for renal failure in elderly patients. Arch Intern Med 163:356-360, 2003.
14. Launay-Vacher V, Izzedine H, Rey JB, et al: Incidence of renal insufficiency in cancer patients and evaluation of information available on the use of anticancer drugs in renally impaired patients. Med Sci Monit 10:CR209-212, 2004.
15. Sokoll LJ, Russell RM, Sadowski JA, et al: Establishment of creatinine clearance reference values for older women. Clin Chem 40:2276-2281, 1994.
16. Cockcroft DW, Gault MH: Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron 16:31-41, 1976.
17. Marx GM, Blake GM, Galani E, et al: Evaluation of the Cockroft-Gault, Jelliffe and Wright formulae in estimating renal function in elderly cancer patients. Ann Oncol 15:291-295, 2004.
18. Aapro M, Launay-Vacher V, Lichtman S, et al: A report from a SIOG Task Force on Renal Safety in the Elderly. International Society of Geriatric Oncology Newsletter. 1(1):1, 2005. Available at www.cancerworld.org/cancerworldadmin/getStaticModFileaspx?id =893. Accessed May 4, 2006.
19. Trimble EL, Carter CL, Cain D, et al: Representation of older patients in cancer treatment trials. Cancer 74:2208-2214, 1994.
20. Kemeny MM, Peterson BL, Kornblith AB, et al: Barriers to clinical trial participation by older women with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 21:2268-2275, 2003.
21. Sateren WB, Trimble EL, Abrams J, et al: How sociodemographics, presence of oncology specialists, and hospital cancer programs affect accrual to cancer treatment trials. J Clin Oncol 20:2109-2117, 2002.
22. Andre T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L, et al: Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med 350:2343-2351, 2004.
23. Gill S, Loprinzi CL, Sargent DJ, et al: Pooled analysis of fluorouracil-based adjuvant therapy for stage II and III colon cancer: Who benefits and by how much? J Clin Oncol 22:1797-1806, 2004.
24. Laurie JA, Moertel CG, Fleming TR, et al: Surgical adjuvant therapy of large-bowel carcinoma: An evaluation of levamisole and the combination of levamisole and fluorouracil. The North Central Cancer Treatment Group and the Mayo Clinic. J Clin Oncol 7:1447-1456, 1989.
25. Moertel CG, Fleming TR, Macdonald JS, et al: Levamisole and fluorouracil for adjuvant therapy of resected colon carcinoma. N Engl J Med 322:352-358, 1990.
26. NIH Consensus Conference: Adjuvant therapy for patients with colon and rectal cancer. JAMA 264:1444-1450, 1990.
27. Schrag D, Cramer LD, Bach PB, et al: Age and adjuvant chemotherapy use after surgery for stage III colon cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 93:850-857, 2001.
28. Schrag D, Gelfand SE, Bach PB, et al: Who gets adjuvant treatment for stage II and III rectal cancer? Insight from Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results-Medicare. J Clin Oncol 19:3712-3718, 2001.
29. Sundararajan V, Grann VR, Jacobson JS, et al: Variations in the use of adjuvant chemotherapy for node-positive colon cancer in the elderly: A population-based study. Cancer J 7:213-218, 2001.
30. Mahoney T, Kuo YH, Topilow A, et al: Stage III colon cancers: Why adjuvant chemotherapy is not offered to elderly patients. Arch Surg 135:182-185, 2000.
31. Potosky AL, Harlan LC, Kaplan RS, et al: Age, sex, and racial differences in the use of standard adjuvant therapy for colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 20:1192-1202, 2002.
32. Haller DG, Catalano PJ, Macdonald JS, et al: Phase III study of fluorouracil, leucovorin, and levamisole in high-risk stage II and III colon cancer: Final report of Intergroup 0089. J Clin Oncol 23:8671-8678, 2005.
33. Sargent DJ, Goldberg RM, Jacobson SD, et al: A pooled analysis of adjuvant chemotherapy for resected colon cancer in elderly patients. N Engl J Med 345:1091-1097, 2001.
34. Jessup JM, Stewart A, Greene FL, et al: Adjuvant chemotherapy for stage III colon cancer: Implications of race/ethnicity, age, and differentiation. JAMA 294:2703-2711, 2005.
35. Folprecht G, Cunningham D, Ross P, et al: Efficacy of 5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy in elderly patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: A pooled analysis of clinical trials. Ann Oncol 15:1330-1338, 2004.
36. Iversen LH, Pedersen L, Riis A, et al: Age and colorectal cancer with focus on the elderly: Trends in relative survival and initial treatment from a Danish population-based study. Dis Colon Rectum 48:1755-1763, 2005.
37. Tsalic M, Bar-Sela G, Beny A, et al: Severe toxicity related to the 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin combination (the Mayo Clinic regimen): A prospective study in colorectal cancer patients. Am J Clin Oncol 26:103-106, 2003.
38. Patel K, Anthoney DA, Crellin AM, et al: Weekly 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin: Achieving lower toxicity with higher dose-intensity in adjuvant chemotherapy after colorectal cancer resection. Ann Oncol 15:568-573, 2004.
39. Scheithauer W, McKendrick J, Begbie S, et al: Oral capecitabine as an alternative to I.V. 5-fluorouracil-based adjuvant therapy for colon cancer: Safety results of a randomized, phase III trial. Ann Oncol 14:1735-1743, 2003.
40. Twelves C, Wong A, Nowacki MP, et al: Capecitabine as adjuvant treatment for stage III colon cancer. N Engl J Med 352:2696-2704, 2005.
41. Diaz-Rubio E, Burris H, Douillard JY, et al: Safety of capecitabine (X) compared to fluorouracil/leucovorin (5-FU/LV) for the adjuvant treatment of elderly colon cancer patients (pts) (abstract 3737). J Clin Oncol 22(14S):258s, 2004.
42. Sargent D, Goldberg RM, Bleiberg H, et al: A pooled analysis to assess safety and efficacy of the FOLFOX4 regimen (bi-monthlyoxaliplatin plus fluorouracil/leucovorin) in elderly patients with colorectal cancer. Proceedings of the World Congress of Gastrointestinal Cancer, Barcelona, page O-007, 2005.
43. Tournigand C, Cervantes A, Figer A, et al: OPTIMOX1: A randomized study of FOLFOX4 or FOLFOX7 with oxaliplatin in a stop-and-go gashion in advanced colorectal cancer-a GERCOR study. J Clin Oncol 24:394-400, 2006.
44. Popescu RA, Norman A, Ross PJ, et al: Adjuvant or palliative chemotherapy for colorectal cancer in patients 70 years or older. J Clin Oncol 17:2412-2418, 1999.
45. Tournigand C, Andre T, Achille E, et al: FOLFIRI followed by FOLFOX6 or the reverse sequence in advanced colorectal cancer: A randomized GERCOR study. J Clin Oncol 22:229-237, 2004.
46. Rothenberg ML, Cox JV, DeVore RF, et al: A multicenter, phase II trial of weekly irinotecan (CPT-11) in patients with previously treated colorectal carcinoma. Cancer 85:786-795, 1999.
47. Douillard JY, Cunningham D, Roth AD, et al: Irinotecan combined with fluorouracil compared with fluorouracil alone as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: A multicentre randomised trial. Lancet 355:1041-1047, 2000.
48. Souglakos J, Pallis A, Kakolyris S, et al: Combination of irinotecan (CPT-11) plus 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin (FOLFIRI regimen) as first line treatment for elderly patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: A phase II trial. Oncology 69:384-390, 2005.
49. Sastre J, Marcuello E, Masutti B, et al: Irinotecan in combination with fluorouracil in a 48-hour continuous infusion as first-line chemotherapy for elderly patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: A Spanish Cooperative Group for the Treatment of Digestive Tumors study. J Clin Oncol 23:3545-3551, 2005.
50. Saltz LB, Cox JV, Blanke C, et al: Irinotecan plus fluorouracil and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. Irinotecan Study Group. N Engl J Med 343:905-914, 2000.
51. Venook AP, Enders Klein C, Fleming G, et al: A phase I and pharmacokinetic study of irinotecan in patients with hepatic or renal dysfunction or with prior pelvic radiation: CALGB 9863. Ann Oncol 14:1783-1790, 2003.
52. Cassidy J, Tabernero J, Twelves C, et al: XELOX (capecitabine plus oxaliplatin): Active first-line therapy for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 22:2084-2091, 2004.
53. de Gramont A, Figer A, Seymour M, et al: Leucovorin and fluorouracil with or without oxaliplatin as first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 18:2938-2947, 2000.
54. Andre T, Bensmaine MA, Louvet C, et al: Multicenter phase II study of bimonthly high-dose leucovorin, fluorouracil infusion, and oxaliplatin for metastatic colorectal cancer resistant to the same leucovorin and fluorouracil regimen. J Clin Oncol 17:3560-3568, 1999.
55. Mattioli R, Massacesi C, Recchia F, et al: High activity and reduced neurotoxicity of bi-fractionated oxaliplatin plus 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin for elderly patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol 16:1147-1151, 2005.
56. Comella P, Natale D, Farris A, et al: Capecitabine plus oxaliplatin for the first-line treatment of elderly patients with metastatic colorectal carcinoma: Final results of the Southern Italy Cooperative Oncology Group trial 0108. Cancer 104:282-289, 2005.
57. Twelves CJ, Butts CA, Cassidy J, et al: Capecitabine/oxaliplatin, a safe and active first-line regimen for older patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: Post hoc analysis of a large phase II study. Clin Colorectal Cancer 5:101-107, 2005.
58. Comandone A, Pochettino P, Bergnolo P, et al: Capecitabine and oxaliplatin: A phase II study with a new schedule of administration in elderly patients with advanced colorectal cancer (abstract 3681). J Clin Oncol 23(16S), 2005.
59. Lopez-Gomez L, Escudero P, Yubero A, et al: XELOX (capecitabine and oxaliplatin) as 1st line treatment for elderly patients (pts) with advanced/metastatic colorectal cancer (MCRC) (abstract 3688). J Clin Oncol 22(14S), 2004.
60. Oh D-Y, Kim Y-J, Han S-W, et al: Efficacy of reduced dose intensity FOLFOX-4 as first line palliative chemotherapy in elderly patients with advanced colorectal cancer (CRC) (abstract 3720). J Clin Oncol 23(16S), 2005.
61. Feliu J, Escudero P, Llosa F, et al: Capecitabine as first-line treatment for patients older than 70 years with metastatic colorectal cancer: An Oncopaz Cooperative Group study. J Clin Oncol 23:3104-3111, 2005.
62. Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, et al: Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 350:2335-2342, 2004.
63. Giantonio BJ, Catalano PJ, Meropol NJ, et al: High-dose bevacizumab improves survival when combined with FOLFOX4 in previously treated advanced colorectal cancer: Results from the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) study E3200 (abstract 2). J Clin Oncol 23(16S):1s, 2005.
64. Hochster HS, Welles L, Hart L, et al: Safety and efficacy of bevacizumab (Bev) when added to oxaliplatin/fluoropyrimidine (O/F) regimens as first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC): Tree 1 & 2 studies (abstract 3515). J Clin Oncol 23(16S), 2005.
65. Mass RD, Fyfe G, Hambleton J, et al: Bevacizumab in combination with 5-FU/leucovorin improves survival in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: A combined analysis (abstract 3616). J Clin Oncol 22(14S), 2004.
66. Kabbinavar FF, Schulz J, McCleod M, et al: Addition of bevacizumab to bolus fluorouracil and leucovorin in first-line metastatic colorectal cancer: Results of a randomized phase II trial. J Clin Oncol 23:3697-3705, 2005.
67. Cunningham D, Humblet Y, Siena S, et al: Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 351:337-345, 2004.
68. Saltz LB, Meropol NJ, Loehrer PJ Sr, et al: Phase II trial of cetuximab in patients with refractory colorectal cancer that expresses the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Clin Oncol 22:1201-1208, 2004.
69. Cunningham D, Humblet Y, Siena S, et al: Cetuximab (C225) alone or in combination with irinotecan (CPT-11) in patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-positive, irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer (MCRC) (abstract 1012). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 22:252, 2003.
70. Tabernero JM, Van Cutsem E, Sastre J, et al: An international phase II study of cetuximab in combination with oxaliplatin/5-fluorouracil (5-FU)/folinic acid (FA) (FOLFOX-4) in the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC) expressing epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Preliminary results (abstract 248). J Clin Oncol 22(14S), 2004.
71. Extermann M, Aapro M, Bernabei R, et al: Use of comprehensive geriatric assessment in older cancer patients: Recommendations from the Task Force on CGA of the International Society of Geriatric Oncology (SIOG). Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 55:241-252, 2005.
72. Hurria A, Gupta S, Zauderer M, et al: Developing a cancer-specific geriatric assessment: A feasibility study. Cancer 104:1998-2005, 2005.