Response to Treatment With Rituximab in a Patient With Acquired von Willebrand Disease
The patient is a 58-year-old woman (AA genotype) who was found to have a prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) of 65.7 seconds during a preoperative evaluation for spinal stenosis surgery and mild rectal bleeding. Her aPTT test repeatedly remained abnormally prolonged. The patient had an aPTT mixing study that did not correct immediately or at 2 hours (56.4 seconds vs control 29.7 seconds). Her bleeding time was also abnormally prolonged at 11 minutes.
The patient is a 58-year-old woman (AA genotype) who was found to have aprolonged activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) of 65.7 seconds during apreoperative evaluation for spinal stenosis surgery and mild rectal bleeding.Her aPTT test repeatedly remained abnormally prolonged. The patient had an aPTTmixing study that did not correct immediately or at 2 hours (56.4 seconds vscontrol 29.7 seconds). Her bleeding time was also abnormally prolonged at 11minutes.
The patient’s factor VIII level was 10%, her von Willebrand factor (vWF)antigen level was 13%, and her vWF ristocetin level was 13% with extremely lowlevels of vW multimers, indicating acquired von Willebrand disease (type III orsevere type I) with an accompanying factor VIII deficiency.
The patient’s dilute Russell’s viper venom test (DRVVT) was normal.Circulating anticoagulant was presumed to be associated with the monoclonalimmunoglobulin (Ig)G-lambda (1,800 mg/dL) discovered on a serum proteinelectrophoresis and immunoprecipitation studies. The patient had a bone marrowbiopsy that showed 10% plasma cells and confirmed diagnosis of monoclonalgammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS).
Because of the planned surgical procedures, the patient was treated withcorticosteroids. She failed to respond to prednisone at 1 mg/kg for 2 weeks andIV immunoglobulin (1 g/kg/d × 2 infusion) treatment. In light of recent reportsof successful treatment of autoimmune diseases refractory to standard therapy,such as immune thrombocytopenic purpura, with rituximab (Rituxan), we tried thefollowing regimen on this patient: rituximab at 375 mg/m² IV administered weeklyfor 4 weeks for two cycles. After treatment, the patient’s aPTT, bleedingtime, and factor VIII levels normalized; however, she relapsed and wassuccessfully re-treated. Pre- and posttreatment levels are provided in the following table:
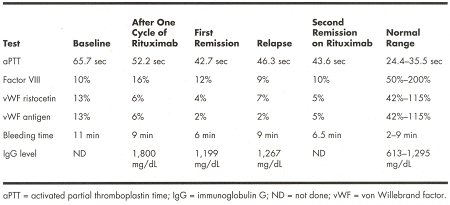
CONCLUSION: To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time rituximabhas been used to treat acquired von Willebrand disease secondary toautoantibodies. The response stopped the patient’s clinical bleeding. She hada partial response in her laboratory measurements, with correction of bleedingtime and improved but still prolonged aPTT, while her von Willebrand parametersremained low. She relapsed after a year and a second response was observed byre-treatment with rituximab.
Click here to read Dr. Bruce Cheson's commentary on this abstract.