13 The Cause and Eradication of Breast Cancer
Background
Almost all women with breast cancer have dermatofibromas.
Methods
Five women with breast cancer had their dermatofibromas excised and tested for arsenic. A total of 56 women with breast cancer and 56 women without breast cancer were examined for the presence of dermatofibromas.
Results
The Cause of Breast Cancer
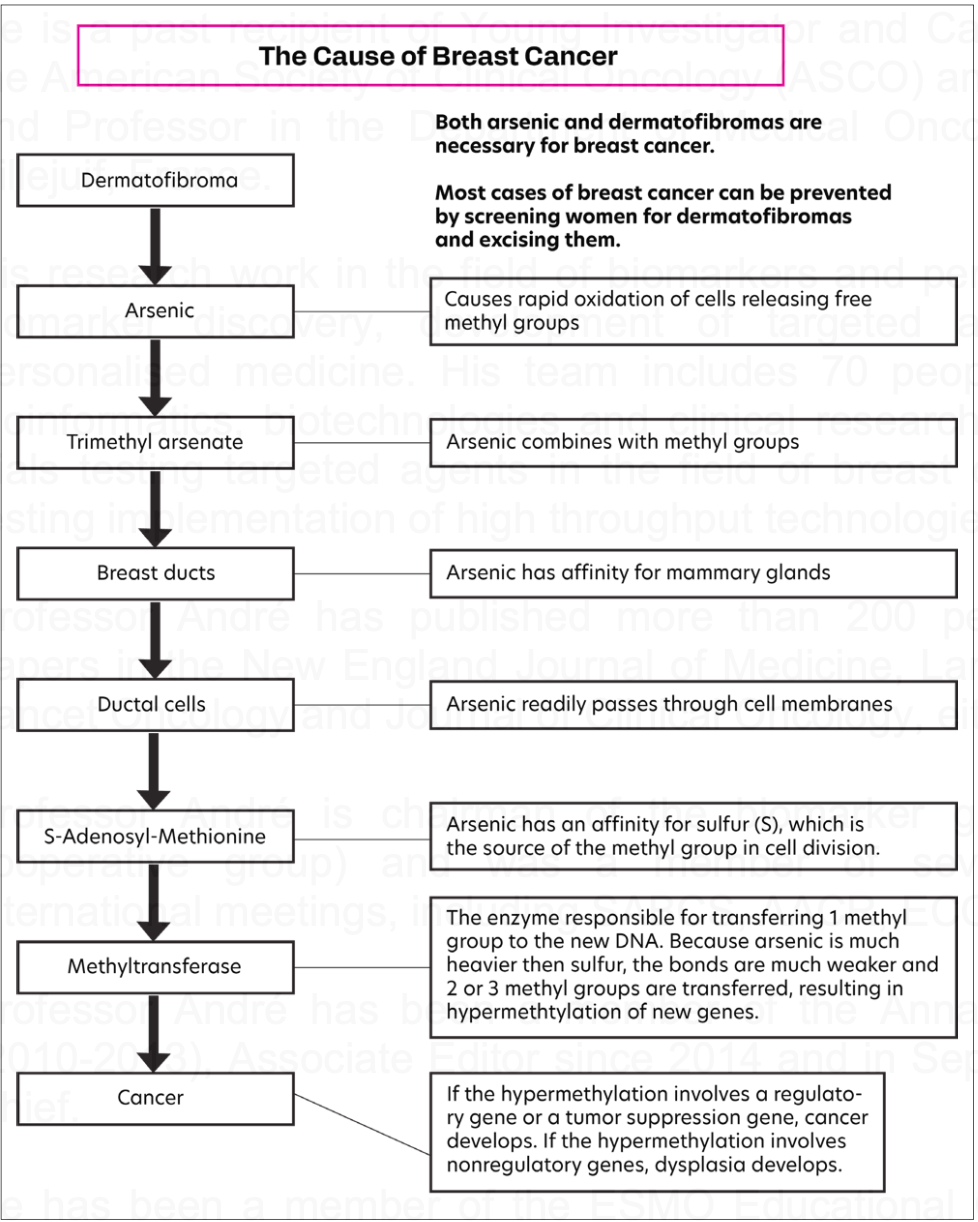
Dermatofibromas were found to have a lethal amount of arsenic. Either the dermatofibroma was caused by arsenic or became a reservoir to trap arsenic. Women with breast cancer and multiple dermatofibromas (n = 38) had a 100% chance of getting the disease. Women with 1 dermatofibroma (n = 11) had a 60% chance of getting the disease. Women with no dermatofibromas (n = 7) had only a 12% chance of getting the disease. In the group without breast cancer, 47 of 56 patients had no dermatofibromas and none had multiple dermatofibromas. Nine patients had 1 dermatofibroma but, as shown by the Figure, had protection by not following every step (probability).
Conclusion
Dermatofibromas are caused by arsenic and set off a cascade of events leading to breast cancer. Screening women in their 20s, 30s, and 40s for dermatofibromas and removing them should eradicate at least 80% to 90% of breast cancer cases.

Giredestrant Combo Yields Positive PFS in Subgroups After CDK4/6i in ER+/HER2– Breast Cancer
December 13th 2025“The magnitude of clinical benefit was clinically meaningful and consistent, and was regardless of PIK3CA mutations or alterations in the PIK3CA pathway, duration of prior CDK4/6 inhibitors, including patients who progress within 6 to 12 months, and the choice of prior CDK4/6 inhibitors,” said Hope S. Rugo, MD.