24 Patient Preferences for CDK4/6 Inhibitor Treatments in HR+/HER2– Early Breast Cancer: A Discrete Choice Survey Study
Background
Patients with stage II/III hormone receptor–positive (HR+)/HER2-negative (HER2–) early breast cancer (EBC) are at risk of recurrence that persists over years. The addition of a CDK4/6 inhibitor to adjuvant endocrine therapy (ET) was studied in the phase 3 monarchE trial, which assessed abemaciclib (ABE), and the phase 3 NATALEE trial (NCT03701334), which assessed ribociclib (RIB). Abemaciclib was FDA approved for this indication in 2021, and NATALEE recently reported statistically significant invasive disease-free survival (iDFS) results. This study evaluated the extent to which patients in the United States value treatment attributes and how these translate into preferences among 2 CDK4/6 inhibitors, ribociclib, and abemaciclib.
Methods
A web-based discrete choice experiment survey was conducted from January to May 2023. Patients were adult women with self-reported stage II/III HR+/HER2– EBC with or without prior chemotherapy receiving only adjuvant ET at the time of the survey. Patients selected scenarios from choice cards, each with 2 hypothetical treatment profiles. A total of 8 attributes related to efficacy (5-year iDFS), adverse effects (AEs; risk of diarrhea, fatigue, or venous thromboembolic events [VTE]), monitoring (number of electrocardiograms [EKG] or blood tests), treatment duration (2 years vs 3 years), and schedule (once daily, intermittent vs twice daily, continuous) were included. A conditional logistic regression model was used to estimate the relative importance (RI) of each attribute. Utility scores were estimated for the model with various scenarios tested.
Results
Survey Results
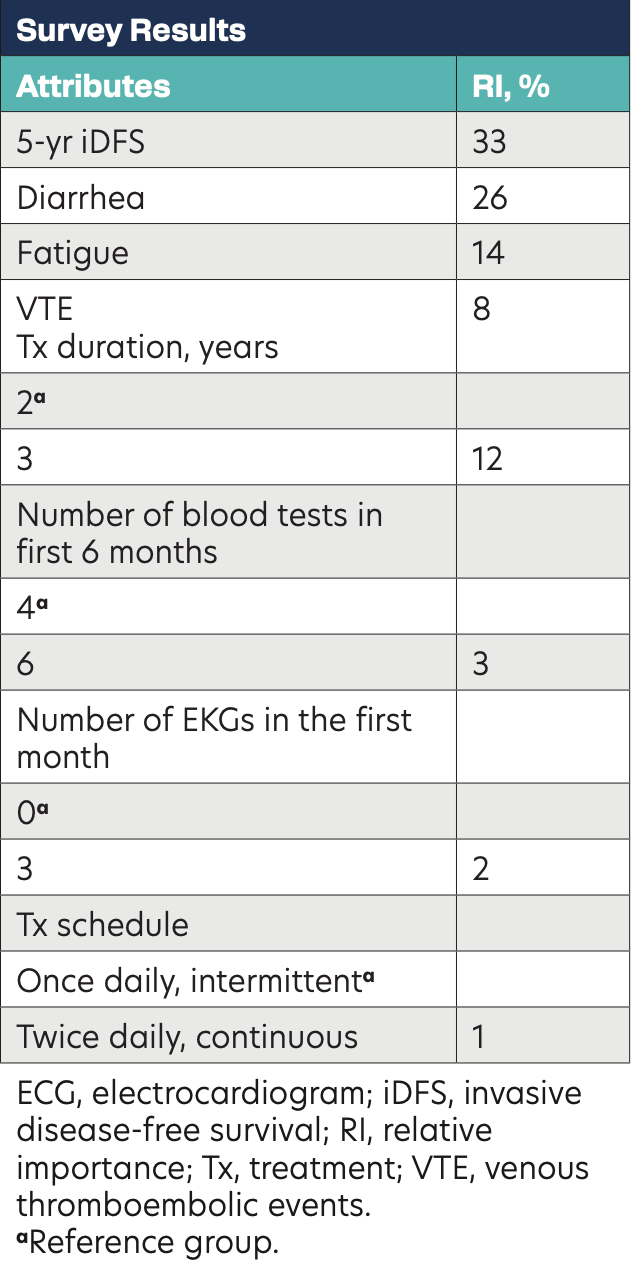
A total of 409 patients participated in the survey (median age,
53 years; White/Black/other race, 59%/23%/23%; BC stage II/III, 48%/52%; employed, 38%). Patient preferences for attributes in order of high to low RI were 5-year iDFS, risk of diarrhea, risk of fatigue, shorter treatment duration, and risk of VTE. The number of blood tests, number of EKGs, and treatment schedule did not affect treatment choice. Overall utility scores were consistently higher for treatment profiles that resembled RIB features, including in conservative scenarios where efficacy was assumed to be equivalent/lower with ABE.
Conclusions
This study showed that driven by a preference for lower risk of AEs, patients prefer treatment profiles that more closely resemble the clinical experience with ribociclib. These patient preferences are important for shared decision-making when considering the addition of a CDK4/6 inhibitor to adjuvant treatment for patients with HR+/HER2– EBC.
