32 Neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab or Placebo Plus Chemotherapy Followed by Adjuvant Pembrolizumab or Placebo for Early-Stage Triple- Negative Breast Cancer: Updated Event-Free Survival Results From the Phase 3 KEYNOTE-522 Study
Background
In KEYNOTE-522, neoadjuvant pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy followed by adjuvant pembrolizumab showed statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in pathological complete response (pCR) and event-free survival (EFS) compared with neoadjuvant placebo plus chemotherapy followed by adjuvant placebo in patients with early-stage triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). Here, we present updated EFS results after a median follow-up of about 5 years.
Methods
Eligible patients with previously untreated, nonmetastatic, centrally confirmed TNBC (stage T1c N1-2 or T2-4 N0-2 per American Joint Committee on Cancer) were randomly assigned 2:1 to neoadjuvant pembrolizumab at 200 mg every 3 weeks or placebo, both given with 4 cycles of paclitaxel plus carboplatin, then with 4 cycles of doxorubicin or epirubicin plus cyclophosphamide. After definitive surgery, patients received adjuvant pembrolizumab or placebo for 9 cycles or until recurrence or unacceptable toxicity. Dual primary end points were pCR (ypT0/Tis ypN0) and EFS (time from randomization to disease progression that precluded definitive surgery, local/distant recurrence, second primary cancer, or death from any cause).
Results
EFS Results in the Overall Population and by Subgroup Pembrolizumab plus Chemotherapy
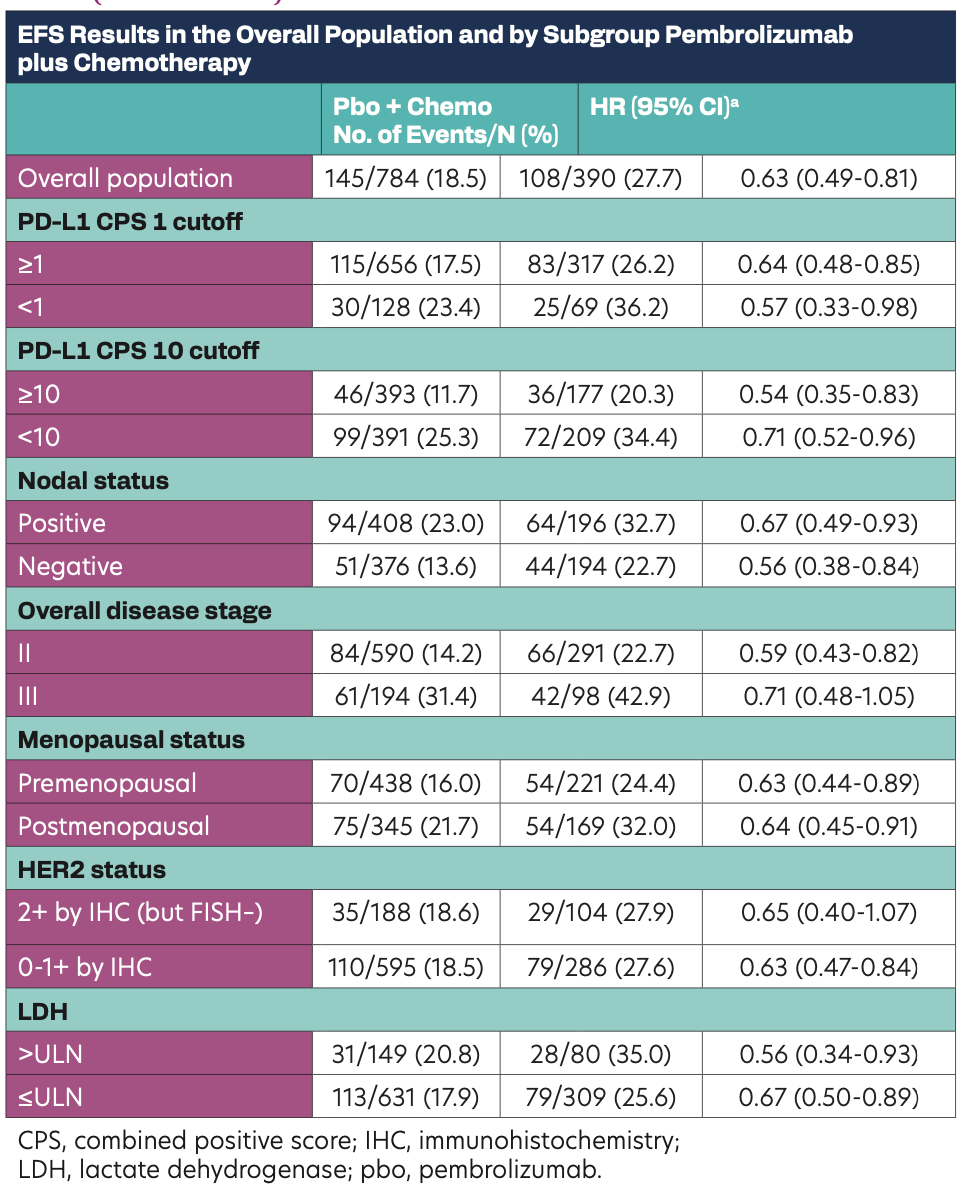
A total of 1174 patients were randomly assigned to pembrolizumab (n = 784) or placebo (n = 390). At the data cutoff (March 23, 2023), the median follow-up was 63.1 months. Additionally, 145 patients (18.5%) in the pembrolizumab group and 108 patients (27.7%) in the placebo group had an EFS event (HR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.49-0.81). The 60-month EFS rate was 81.3% (95% CI, 78.4-83.9) vs 72.3% (95% CI, 67.5-76.5), respectively; the median was not reached in either group. The benefit of neoadjuvant pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy followed by adjuvant pembrolizumab
vs neoadjuvant chemotherapy alone was consistent with the primary EFS results in all 5 sensitivity analyses, showing durable and robust EFS benefit in the pembrolizumab arm. The EFS benefit with pembrolizumab was consistent across prespecified subgroups, including PD-L1 expression, nodal status, disease stage, menopausal status, HER2 status, and lactate dehydrogenase level (Table). In a prespecified, nonrandomized, exploratory analysis, 5-year EFS rates in the pembrolizumab and placebo groups were 92.2% vs 88.2% in patients with a pCR, and 62.6% vs 52.3% in patients without a pCR. Additional analyses will be included in the presentation. Follow-up for overall survival is ongoing.
Conclusions
Neoadjuvant pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy followed by adjuvant pembrolizumab continues to show a clinically meaningful improvement in EFS compared with neoadjuvant chemotherapy alone in patients with early-stage TNBC. This is seen across subgroups and regardless of the pCR outcome.
