42 Exploring the Treatment Gap in High-Risk HR+, HER2– Early Breast Cancer: Eligible Patients Not Receiving Abemaciclib in the US
42 Exploring the Treatment Gap in High-Risk HR+, HER2– Early Breast Cancer: Eligible Patients Not Receiving Abemaciclib in the US

Background
Real-world risk of recurrence in patients with node-positive, hormone receptor–positive (HR+), HER2-negative (HER2–) early breast cancer who have N1 disease with additional high-risk features or N2/N3 disease is 29% at 5 years when treated with standard adjuvant endocrine therapy (ET). Adjuvant abemaciclib plus ET is approved and recommended for these patients to reduce the risk of recurrence, with about 8% lower rate of recurrence at 5 years vs ET alone. Retrospective, single-institution studies have reported adjuvant abemaciclib utilization rates of about 50% in eligible patients. This real-world study describes characteristics of eligible patients not receiving adjuvant abemaciclib across more than 250 US cancer clinics.
Materials and Methods
This retrospective study used the US nationwide Flatiron Health electronic health record-derived de-identified database. Adult patients with HR+, HER2–, node-positive, early breast cancer (stage IA-IIIC) who underwent breast cancer surgery and then initiated adjuvant ET-based therapy from January 2023 to March 2024 were selected. N1/N1mi disease was Grade 3 or 5 cm or more. Adjuvant abemaciclib use was assessed through June 2024. The database does not capture comorbidities, financial considerations, or patient/physician discussion. Baseline characteristics were summarized descriptively.
Results
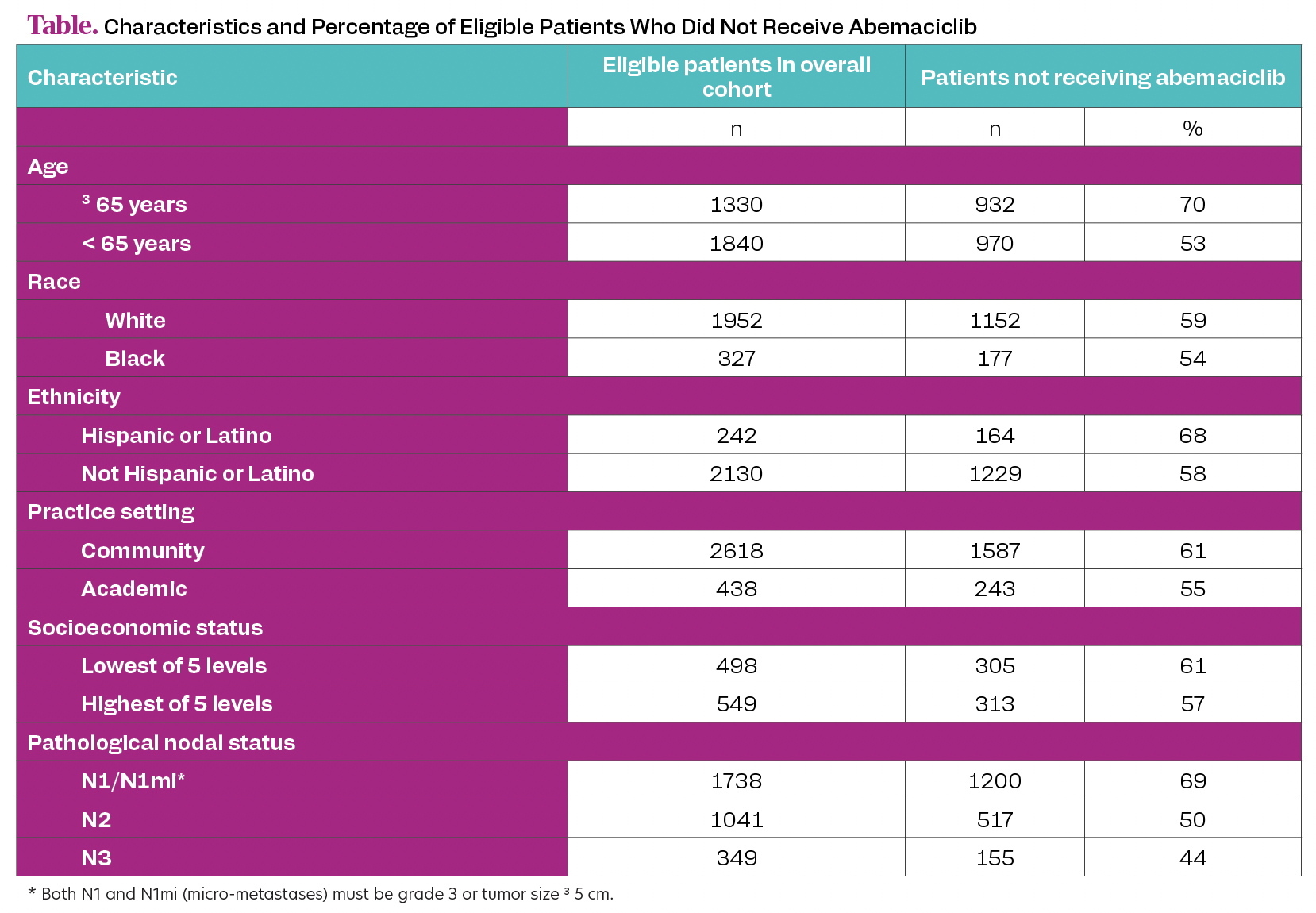
Overall, 3170 patients met eligibility criteria. Median age was 62 years (IQR, 51-71). Patients were mostly female (98%), White (62%) and treated in a community setting (83%). Median follow-up was 9 months (IQR, 6-12).Of eligible patients, 1902 (60%) did not receive abemaciclib; characteristics are summarized (Table). Older age and N1 disease were associated with highest percentage of not receiving abemaciclib.
Table. Characteristics and Percentage of Eligible Patients Who Did Not Receive Abemaciclib
Conclusion
In this real-world study, 60% of patients with node-positive, high-risk HR+, HER2– early breast cancer meeting eligibility criteria for adjuvant abemaciclib did not receive this recommended therapy. The most affected subgroups were older patients (who had similar efficacy and adverse effect rates as younger patients in the phase 3 monarchE trial [NCT03155997]) and patients with N1 plus high-risk features (who have a 2-fold or more recurrence risk vs patients with N1 disease without these high-risk features). Education on recurrence risk and consistent benefit of adjuvant abemaciclib in the approved node-positive, high-risk early breast cancer population, may increase abemaciclib utilization to optimize treatment and prevent incurable metastatic disease.
