44 Variant of Uncertain Significance (VUS) Genetic Testing Results and Mastectomy Choice in Lumpectomy-Eligible Patients
Background
Taken alone, germline genetic variants of uncertain significance (VUS) should not change surgical decision-making in patients with breast cancer (BC) based on current guidelines. We sought to evaluate whether VUS may be a driver of surgical choice in patients with BC who are lumpectomy eligible.
Methods
Patient and Clinical Characteristics by Surgical Choice
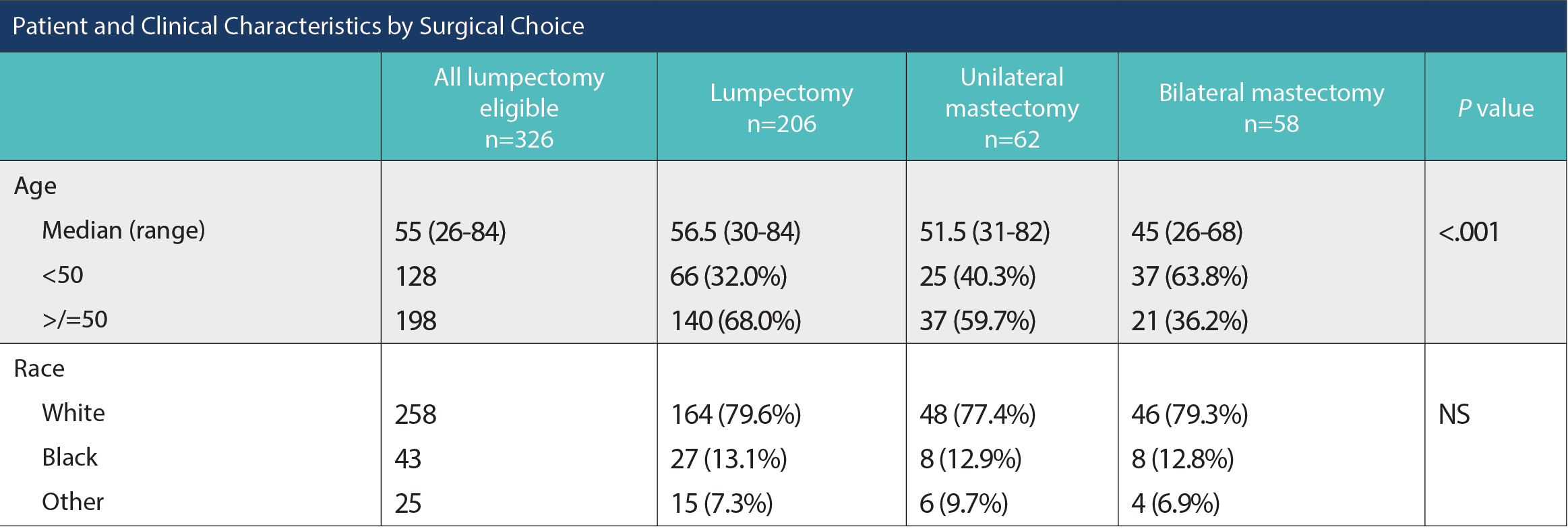
A single-institution retrospective analysis included patients with nonmetastatic BC who underwent lumpectomy or mastectomy from April 2020 to November 2021. We defined “lumpectomy eligible” as unilateral clinical T0-2 nonrecurrent disease in patients able to receive radiation. Patients with known pathogenic mutations were excluded. Descriptive analyses employed chi-square tests to compare patients undergoing lumpectomy or bilateral mastectomy (BLMast) for unilateral early-stage breast cancer, accounting for genetic testing receipt and results among all patients who were lumpectomy-eligible. Multivariate analysis to predict the likelihood of the primary outcome, mastectomy receipt, was limited to tested patients without pathogenic mutations using binomial logistic regression.
Results
Patient and Clinical Characteristics by Surgical Choice (cont.)
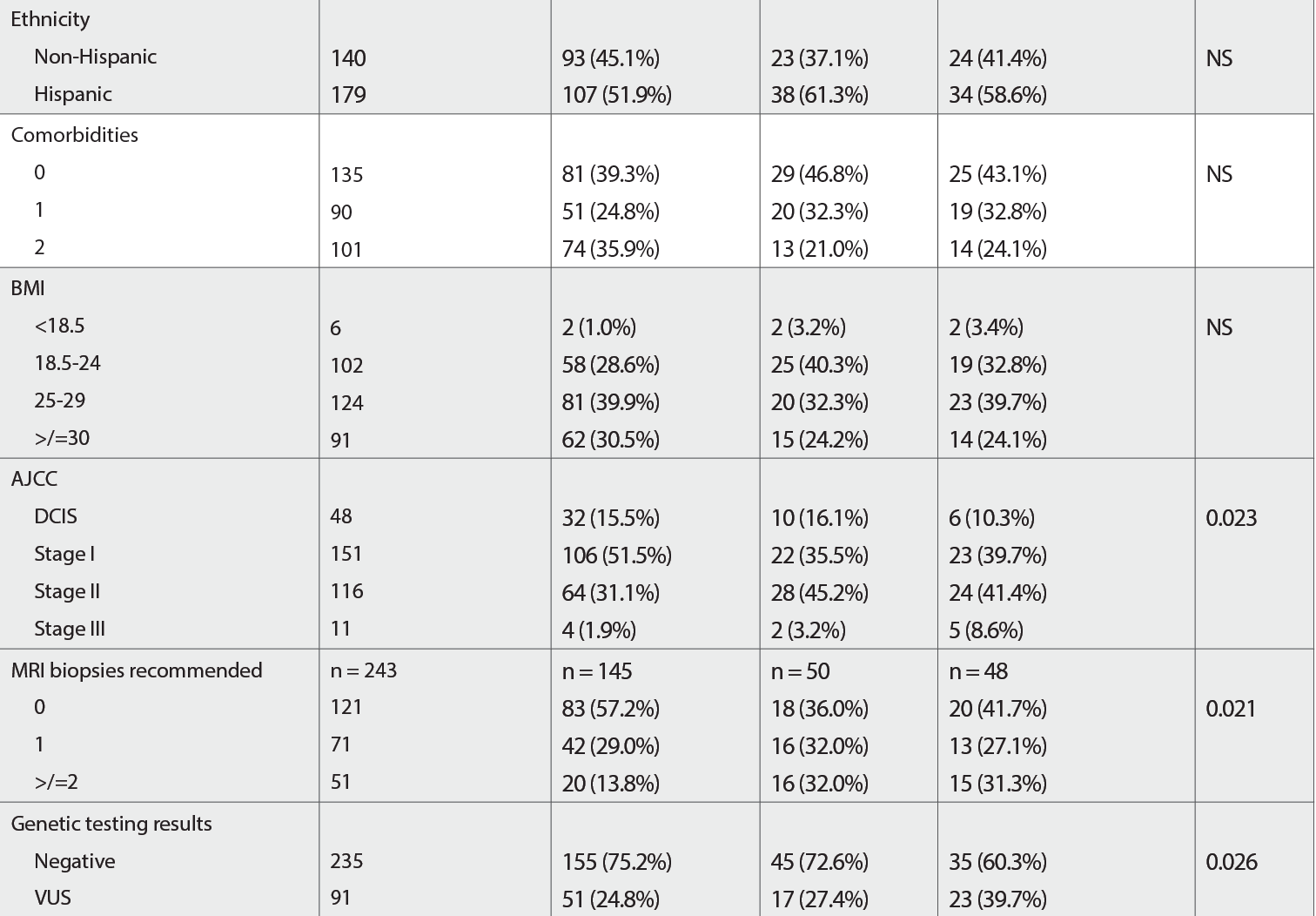
Of 741 patients with BC who had surgical intervention, 549 (74.1%) were lumpectomy eligible and 326 received genetic testing (235 negative, 91 VUS). Overall, the median age was 55.0 (26-84). Of those tested, 206 underwent lumpectomy, and 58 underwent BLMast. Insurance type, race, ethnicity, language, income, tobacco use, marital status, and axillary management did not significantly differ between those who underwent lumpectomy or BLMast. Compared with patients who underwent a lumpectomy, a higher proportion of patients with a VUS result (39.7% vs 24.8%, P = .026), American Joint Committee on Cancer stage II disease (41.4% vs 31.1%, P = .023) and those with 2 or more MRI-recommended preoperative biopsies (31.3% vs 13.8%, P = .021) underwent BLMast. In addition, a significantly higher proportion of patients who underwent BLMast were younger than 50 years (63.8% vs 32.0%, P < .001).
Conclusions
VUS genetic testing results are more prevalent in lumpectomy-eligible patients choosing bilateral mastectomy, along with younger age, higher stage, and MRI biopsy receipt. The present analysis informs the implementation of robust but accessible genetic counseling education initiatives in breast surgical oncology to decrease unnecessary mastectomies in patients
with VUS.
