51 Ductal Carcinoma In Situ With Microinvasion on Biopsy—What Are the Predictors of Upstaging?
Background
Ductal carcinoma in situ with microinvasion (DCISM) follows the same management as used for DCIS. Breast-conserving surgery without sentinel lymph node biopsy is indicated, as the risk of upstaging to invasive carcinoma (> 1 mm) is low. Interestingly, it is reported that approximately 30% of patients with DCISM on biopsy will upstage to invasive cancer, creating a challenge in balancing the risk of overtreatment to undertreatment. The aim of this study is to identify risk factors for upstaging of DCISM to invasive disease (> 1 mm).
Methods
A retrospective chart review of women over the age of 18 years who had a DCISM on initial breast biopsy from 2013 to 2019 at a large single-center institution was performed. Demographic, clinical, histologic, and radiographic data were collected. Descriptive statistics were used to report means and standard deviations. Fisher exact test was used for categorical variables, and the Student t test was used for numerical variables to identify variables that may be associated with final pathologic upstaging.
Results
Patient Characteristics
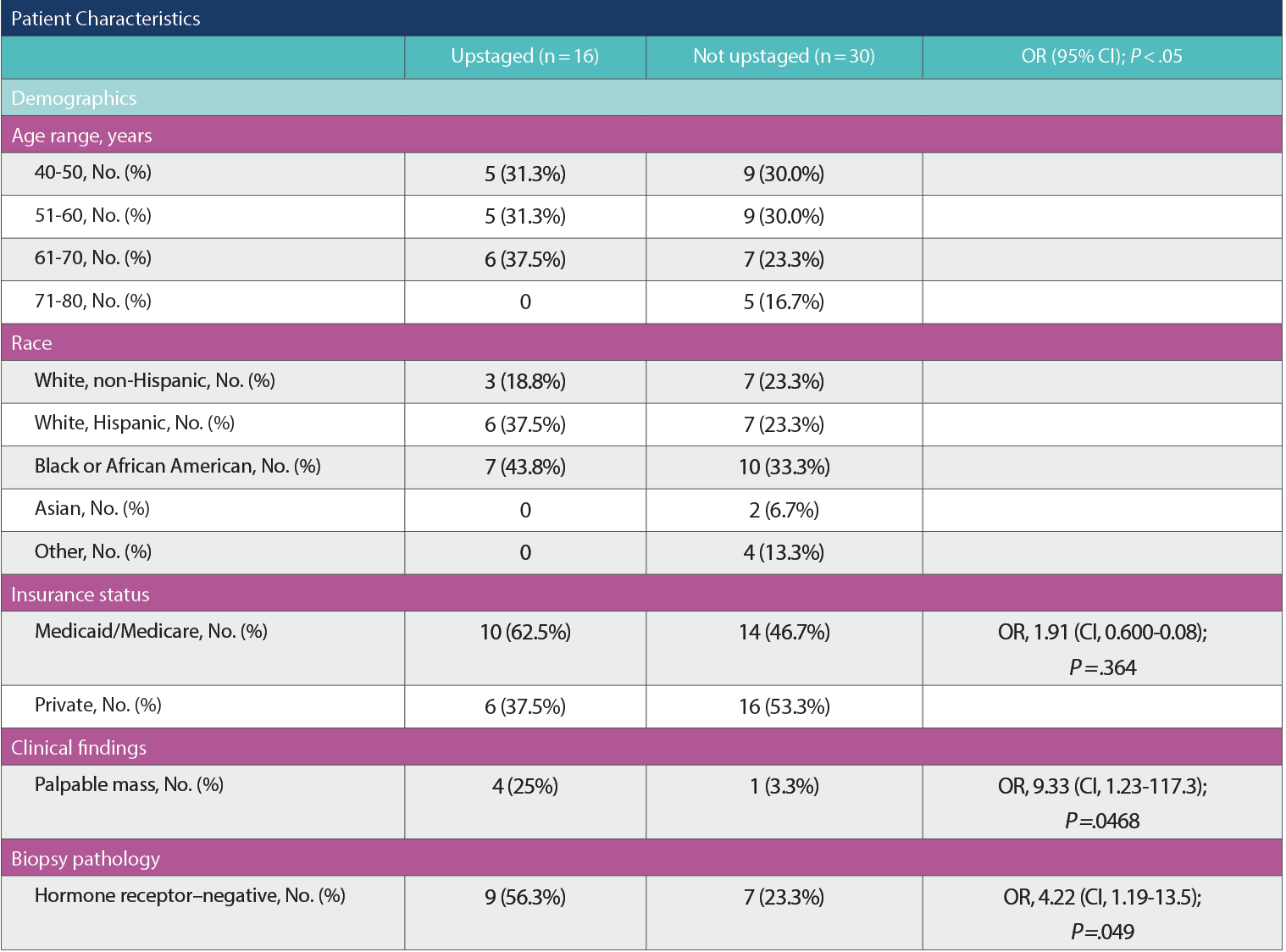
A total of 46 women were identified in the age range of 41 to
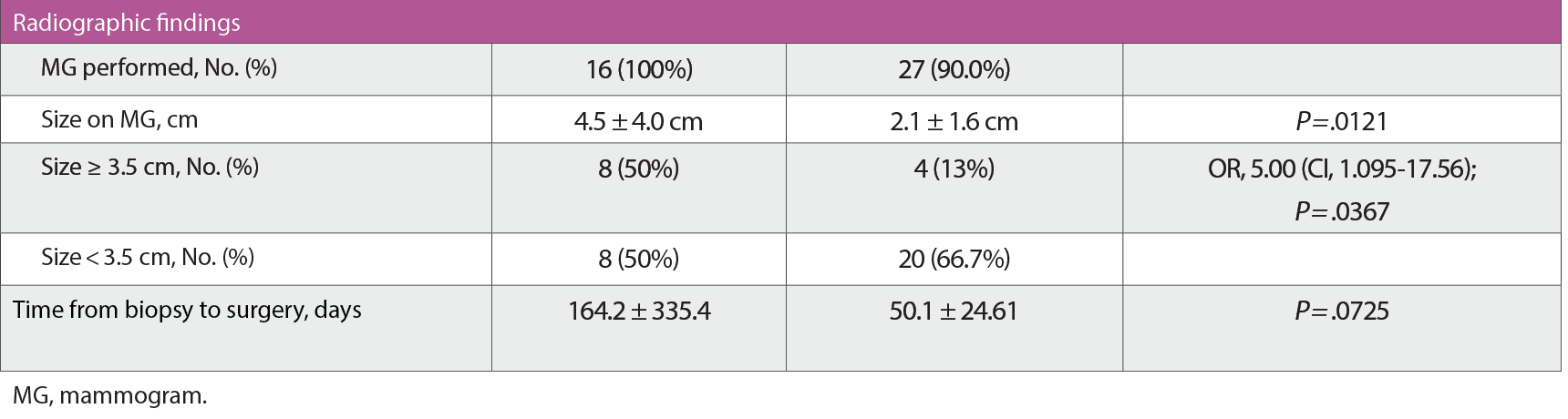
76 years. Sixteen patients (35%) with DCISM on biopsy were upstaged to invasive carcinoma (> 1 mm). Upstaging to invasive disease was correlated with palpable mass (OR, 9.33; CI, 1.23-117.3; P = .0468), hormone receptor negativity on biopsy (OR, 4.22; CI, 1.19-13.5; P = .049), and size on diagnostic mammogram of at least 3.5 cm (OR, 5.00; CI, 1.095-17.56; P = .0367).
Radiographic findings
Conclusions
We report a similar rate of upstaging as previous studies; however, to our knowledge, we are the first to report associated risk factors with upstaging to invasive carcinoma (> 1 mm) from DCISM on biopsy. This can guide surgeons to identify which patients may require a sentinel lymph node biopsy at the time of breast-conserving surgery.
