97 Treatment Discontinuation Among Patients With Stage IV HER2–Negative Breast Cancer
97 Treatment Discontinuation Among Patients With Stage IV HER2–Negative Breast Cancer

Background
To describe treatment discontinuation among patients with stage IV HER2-negative (HER2) breast cancer from first to fourth line of treatment (LOT) based on electronic medical records across 3 academic cancer centers in the US.
Materials and Methods
This was a retrospective cohort study of adult patients with stage IV HER2– breast cancer who started their first LOT between 2017 and 2021 at Huntsman Cancer Institute, H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center & Research Institute, or Winthrop P. Rockefeller Cancer Institute. Patient data were extracted via chart review. The rate of and reasons for discontinuation were analyzed descriptively. Time to next treatment (TTNT) was estimated using Kaplan-Meier methods with censoring at the date of the last follow-up or December 31, 2021, whichever earlier.
Results
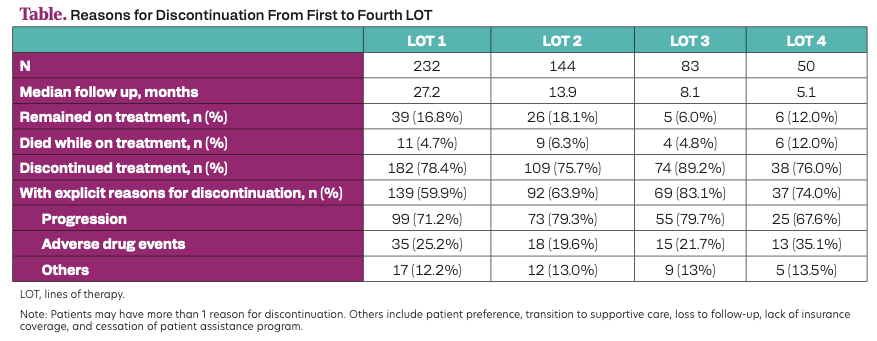
A total of 232 patients were analyzed with a median age (IQR) of 56.6 years (47.8-67.5). 85.8% had hormone receptor–positive (HR+) breast cancer. At each LOT, less than 75% of patients discontinued, of which 20-30% did not receive a subsequent LOT (1st LOT: 21%; 2nd LOT: 24%; 3L: 32%). Among patients with documented reasons for discontinuation, disease progression was most common at between 67.6% and 79.7%, followed by adverse drug events between 19.6% and 35.1% (Table). TTNT decreased with LOT for patients with HR+ breast cancer from 14.8 months at the first LOT to 7.0 months and 4.4 months at the second and third LOT, respectively, and ranged between 4.1 months to 5.2 months for those with HR-negative breast cancer across LOT.
Table. Reasons for Discontinuation From First to Fourth LOT
Conclusion
The attrition rate of 20% to 30% of patients who discontinued treatment after each LOT without subsequent treatment was high among patients with stage IV breast cancer. The most effective treatment options should be used in earlier LOT in this patient population since patients may not receive subsequent LOT.
