Adding oxaliplatin to FULV trends toward better survival in stage II/III colon cancer
CHICAGO-In the adjuvant treatment of colon cancer, addition of oxaliplatin (Eloxatin) to the FULV regimen is associated with a near-significant 15% relative reduction in the risk of death, according to results from a National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project trial (NSABP C-07).
ABSTRACT: Data further suggest that 5 years may be too short to adequately assess differences in overall survival.

CHICAGO-In the adjuvant treatment of colon cancer, addition of oxaliplatin (Eloxatin) to the FULV regimen is associated with a near-significant 15% relative reduction in the risk of death, according to results from a National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project trial (NSABP C-07).
In the trial, patients who had undergone curative resection of stage II or III colon cancer were randomized to the weekly, bolus-based 5-FU/leucovorin regimen alone or with the addition of oxaliplatin, the so-called FLOX regimen, said lead author Norman Wolmark, MD, chairman of human oncology at Allegheny General Hospital, Pittsburgh. The updated analysis was based on 1,209 patients in the FULV arm and 1,200 patients in the FLOX arm; median follow-up was 67 months.
The estimated 5-year rate of disease-free survival (the trial’s primary endpoint) was 64% with FULV and 69% with FLOX, corresponding to a significant 19% relative reduction in the risk of events with the latter regimen (hazard ratio 0.81).
“The advantages we reported previously relative to disease-free survival are very much apparent, are robust, and are durable,” Dr. Wolmark said in a talk at ASCO 2008 (abstract LBA4005). In addition, the benefit was similar in subgroups stratified by age and by number of positive nodes.
The estimated rate of overall survival was 78% with FULV and 80% with FLOX at 5 years, corresponding to a near-significant 15% relative reduction in the risk of death with the latter regimen (HR 0.85, P = .06), and the difference increased at 6 years (74% vs 78%). The actual number of deaths fell short of the predicted number (based on NSABP C-04 results), reducing the trial’s power to detect a difference in this outcome, Dr. Wolmark noted.
The overall survival findings were similar in groups stratified by age and in patients with stage III disease, but in the 29% of patients with stage II disease, the hazard ratio exceeded 1.0. “There are some who have claimed that stage II patients do not have an incremental survival benefit when oxaliplatin is added,” Dr. Wolmark said, showing a forest plot of the subset analyses. “But look at these confidence intervals. They’re enormous. So any story that you make relative to stage II disease is probably fraught with more fable than it is with fact.”
Dr. Wolmark remarked that the overall survival data were nearly identical to those of the MOSAIC adjuvant trial (Andre T et al: N Engl J Med 350:2343-2351, 2004), which tested the addition of oxaliplatin to infusion-based FULV among patients with stage II or III colon cancer.
“The durable consistency between the results of C-07 and MOSAIC validates the benefit of oxaliplatin,” he said.
Longer follow-up needed
In the larger context, he noted, median survival after recurrence has increased significantly
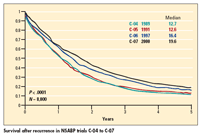
across four recent NSABP trials in stage II/III colon cancer (see Figure). “So clearly, the estimates that were derived from C-04 do not apply to the current generation of adjuvant trials and certainly not the future generation of adjuvant trials,” he said.
He also pointed to another “interesting phenomenon”: In the C-07 trial, median survival after recurrence was significantly better with FULV than with FLOX (22 vs 18 months). “Longer follow-up-certainly greater than 5 years--in future colon cancer adjuvant trials appears to be appropriate to reliably detect a survival benefit,” Dr. Wolmark concluded.