Better Colon Cancer Imaging With PET/CT Than With PET Alone
LOS ANGELES-PET/CT fusion imaging can improve the diagnostic certainty and localization of colorectal cancer, compared with PET alone, according to a retrospective review presented at the 49th Annual Meeting of the Society of
LOS ANGELESPET/CT fusion imaging can improve the diagnostic certainty and localization of colorectal cancer, compared with PET alone, according to a retrospective review presented at the 49th Annual Meeting of the Society of Nuclear Medicine (abstract 78) (see Figure below). "PET alone is not that useful for localization of colorectal cancer," said Christian Cohade, MD, of Johns Hopkins University. "PET/CT is better than PET for diagnostic certainty."
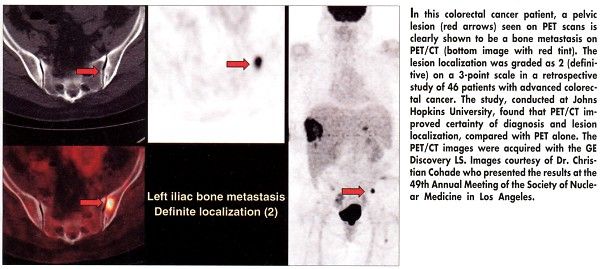
The study included 46 consecutive patients with known advanced colorectal cancer referred for FDG-PET imaging from July to November 2001. Fusion PET/CT images were acquired with the GE Discovery LS. Both PET images and PET/CT images were interpreted independently by two readers blinded as to clinical information.
Lesion localization was graded on a 3-point scale (0 = unknown, 1 = probable, 2 = definitive). A 5-point grading scale was used to evaluate certainty of diagnosisfrom 0 (definitely normal) to 4 (definitely abnormal). Dr. Cohade noted that image evaluation depends in part on the experience of the image reader.
Certainty of diagnosis improved with fusion imaging, compared with PET alone. The number of lesions rated equivocal or probable (probably normal or probably abnormal) was reduced with PET/CT, compared with PET, for both readers (by 44% and 50%). The number of definite diagnoses was increased with PET/CT by 39% and 30% for the two readers, compared with PET alone.
The number of definite lesion localizations was also increased with PET-CT for both readers (66% and 25%).
Although the study clearly showed improvement in certainty of diagnosis and lesion localization with PET/CT on a per lesion basis, further work will be needed to show if this leads to improvements in patient care.
"We need to address the question, In what percentage of patients does using PET/CT change the staging evaluation, compared to PET alone?" Dr. Cohade said. Accordingly, the researchers plan to compare the PET/CT results in this study with the results of the in vivo inspection of the tumors by biopsy or surgery.
Intravenous and oral contrast could be used to help localize and define the lesion in the CT part of the image, Dr. Cohade said.