3 Analysis of Exhaled Volatile Organic Compounds: A New Frontier in Breast Cancer Screening and Surveillance
Alexandra Allard-Coutu BSc, MDCM, FRCSC1; Kevin Singh BSc, MDCM, FRCPC2; André Lamontagne3; Yves Gamache3; Nicole Hodgson MD, FRCSC1; Peter Lovrics MD, FRCSC1; Susan Reid MD, FRCSC1; Barbara Heller MD, FRCSC1
1McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada
2University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada
3eTrace Medical, Montreal, Quebec, Canada
Background
Neoplastic processes cause distinct and immediate changes to the body’s metabolism, creating unique patterns in the volatile organic compounds (VOCs) being produced and released. Unique VOC profiles have been shown to be diagnostic for certain cancers. Exhaled breath VOC analysis has potential as a point-of-care tool for screening a wide range of cancers in a single sample. This technology can also be used to monitor response to treatment and can be applied to posttreatment cancer surveillance protocols.
Methods
An exhaled breath VOC analyzer was developed based on ASDevices and eTrace Medical patented technology. Proof-of-principle experiments established a detection limit and sensitivity/specificity of the Epd sensing technology. A case-control trial is underway to validate the device using 25 exhaled VOCs previously shown to be diagnostic for breast cancer, and assess whether eTrace Medical’s AeolCare point-of-care exhaled breath analyzer accurately predicts a diagnosis of breast cancer in female patients referred for breast biopsy, following abnormal imaging (BI-RADS 3-5) or detection of a palpable breast mass. The ability of the VOC profile to reliably detect breast cancer will be evaluated by receiver operating characteristic curve analysis, followed by cross validation by the leave-one-out method and stepwise logistic regression analysis.
Preliminary Results
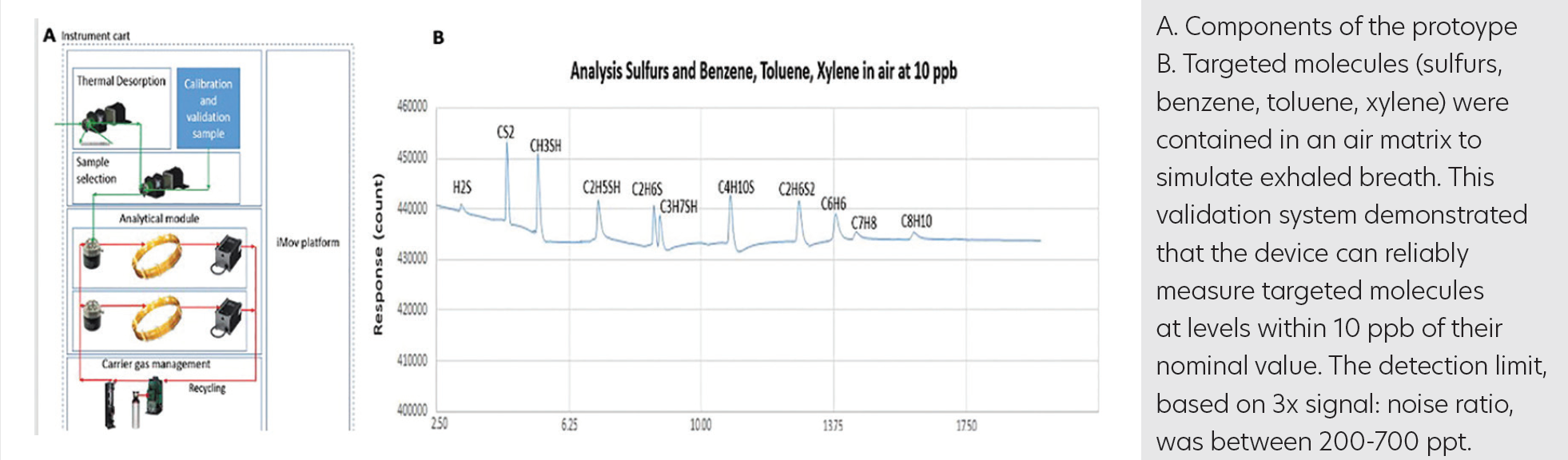
Using representative biomarkers in exhaled breath, proof-of-principle testing confirmed the sensitivity and selectivity of the sensing technology based on a proprietary gas chromatography (GC) method from eTrace Medical (patent pending). Protocol validation included testing of ASDevices technologies (pretreatment and concentrator, iMov GC platform, uInProve GC valve, and Epd sensing technologies) (Figure A). Targeted molecules (sulfur, benzene, toluene, and xylene) were contained in an air matrix to simulate exhaled breath. This validation system demonstrated that the device can reliably measure targeted molecules at levels within 10 ppb of their nominal value (Figure B). The detection limit, based on 3Å~ signal:noise ratio, was between 200 and 700 ppt. The sensitivity of the system can be further adapted via sample concentration and pretreatment.
FIGURE
Conclusion
There is strong evidence to support the use of VOCs in exhaled breath to accurately detect breast cancer. The implementation of VOC analysis for accessible screening and early detection of breast cancer could improve patient outcomes and reduce the number of breast cancer–related deaths, as well as the global disease burden. We propose a proof-of-concept case-control study to determine the sensitivity and specificity of exhaled breath analysis, using a novel point-of-care tool for the diagnosis of breast cancer and previously described VOC breath prints.
