32 Triple-Negative Breast Cancer and Pathological Complete Response: A Study of Racial Disparities
Maithreyi Sarma, MBBS1; Samar Nasir, MD2; Ashwini Ronghe, MD2; Kristopher Atwood, PhD1; Medhavi Gupta, MBBS1; Amy Early, MD1; Tracey O’Connor, MD1; Ellis Levine, MD1; Shipra Gandhi, MD1
1Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, NY.
2State University of New York at Buffalo, School of Medicine & Biomedical Sciences, Buffalo, NY.
Background
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), one of the more aggressive subtypes of breast cancer, is twice as frequent and associated with higher mortality in Non-Hispanic Black (NHB) women compared with non-Hispanic White (NHW) women. Factors contributing to this racial disparity have been shown to include socioeconomic status, insurance variables, delays in diagnosis/treatment, and comorbidities. We examined the association between race and clinical outcomes—pathological complete response (pCR), recurrence-free survival (RFS), and overall survival (OS)—in patients (pts) treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) at our institution.
Materials and Methods
Pts diagnosed with stage I to III TNBC from 2000 through 2018 who received NAC were included in this retrospective study. pCR was considered as absence of residual invasive cancer in the breast and lymph nodes after NAC. Association of race with pCR and survival outcomes were evaluated using logistic and Cox regression models, respectively. Multivariate models were used to evaluate the association between race and pCR or survival while controlling for relevant confounders including age, body mass index (BMI), insurance status, comorbidities, tumor stage, grade, and time from diagnosis to chemotherapy or surgery. Analysis was conducted using SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute) at a significance level of .05.
Results
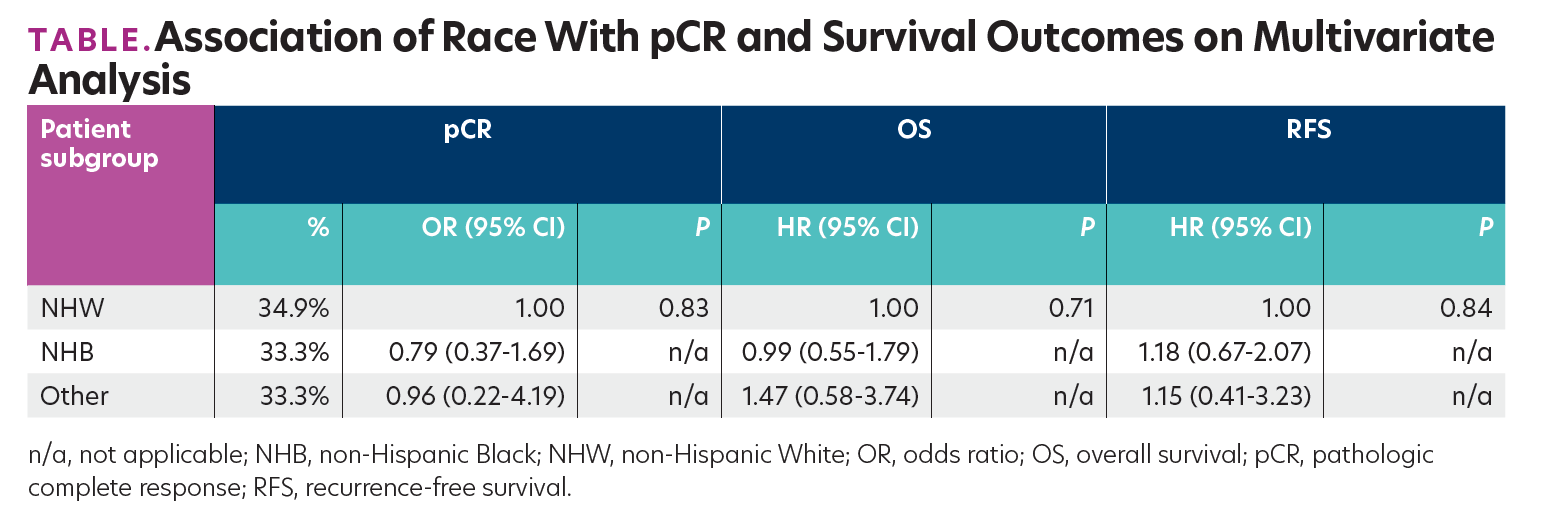
Included in the analysis were 186 pts (126 NHW, 67.7%; 50 NHB, 26.9%; 10 other, 5.4%). NHB pts had higher mean BMI at baseline (32.93 vs 27.45 kg/m2; P <.001), with fewer NHB pts having private insurance than NHW pts (46.0% vs 71.4%; P = .013). No significant association of race with other variables was observed. Pts with pCR were younger at diagnosis (48 vs 52 years; P = .019). Advanced age, higher tumor stage, and longer time from diagnosis to surgery were associated with worse RFS and OS (P <.05). On multivariate analysis, there were no significant associations between race and pCR, RFS, or OS, with similar pCR noted between different races (Table).
TABLE.Association of Race With pCR and Survival Outcomes on Multivariate
Analysis
Conclusions
Our study suggests similar outcomes between races for TNBC treated at a single academic center. Further studies comparing molecular characteristics of TNBC from different races are warranted.
