Thirty percent of clinical trials face zero enrollment
Suppose you hosted a clinical trial and nobody came? That’s what happens 30% of the time, according to researchers from the Center for Management Research in Healthcare at Vanderbilt University in Nashville. “Trials get opened, but no patients are accrued,” said principal investigator David Dilts, PhD.

Suppose you hosted a clinical trial and nobody came? That’s what happens 30% of the time, accordingto researchers from the Center for Management Research in Healthcare at Vanderbilt University in Nashville. “Trials get opened, but no patients are accrued,” said principal investigator David Dilts, PhD.
he study examined accrual rates for all phases of trials opened at four comprehensive cancer centers (CCCs), including Philadelphia’s Fox Chase Cancer Center, Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of North Carolina in Chapel Hill, Ohio State Comprehensive Cancer Center in Columbus, and Vanderbilt-Ingram Comprehensive Cancer Center in Nashville. Th e study also compared accruals to studies sponsored by the Cancer Trials Cooperative Groups (CTCG) and non-CTCG trials at these centers.
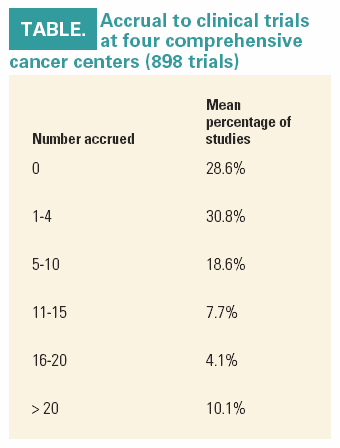
Out of all 898 clinical trials (all phases) conducted at these CCCs, 28.6% had zero accruals (see Table). Studies not sponsored by the CTCG actually were slightly more successful. In those studies, 20.6% accrued zero patients. Five patients or more were accrued to 40.5% of non-CTCG studies and 54.6% of CTCG trials.
Dr. Dilts and his team are now examining characteristics of studies that enrolled the most patients. While waiting for these data, he speculated that one problem is the abundance of competing studies for the same disease state.
“Fashionable” drugs attract greater interest. And the lag time between trial inception and initiation, which can be two to three years, may also be responsible. “By the time some studies open to enrollment, the scientific question is no longer interesting,” he noted.
How Supportive Care Methods Can Improve Oncology Outcomes
Experts discussed supportive care and why it should be integrated into standard oncology care.